Configuring a secure CI/CD pipeline on Amazon Virtual Private Cloud without public internet access

With the growth of the cloud and increasing security awareness, the use of Amazon's private VPCs without public internet access has also increased dramatically. This configuration is recommended to ensure adequate security through isolation. The requirement for isolation also applies to code pipelines, where developers deploy their application modules, software packages, and other dependencies and packages throughout the development cycle. This is done without the need to 'push' larger packages from the development space to the test space or target environment. Furthermore, AWS CodeArtifact is an artifact management service that will help organizations of any size to securely store, publish, and share software packages used in their software development process.
In the following text, we will discuss the steps required to build a secure, private, continuous integration/continuous development (CI/CD) pipeline without public access to the Internet while maintaining log storage in Amazon CloudWatch. We will use AWS CodeCommit as a resource, CodeArtifact for software modules and packages, and Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) as a place to store artifacts.
Prerequisites
Prerequisites to be able to keep up with this article are:
- AWS account
- A virtual private cloud (Amazon VPC)
- The CI/CD pipeline can be CodePipeline, Jenkins, or any CI/CD tool you want to integrate CodeArtifact with. The following tutorial uses CodePipeline.
Description of the solution
The leading service we will focus on is CodeArtifact. This fully managed artifact repository service makes it easy for organizations of any size to securely store, publish, and share software packages used in their software development process. CodeArtifact works with commonly used package managers and compilation tools such as Maven and Gradle (Java), npm and yarn (JavaScript), pip and twine (Python), or NuGet (.NET).
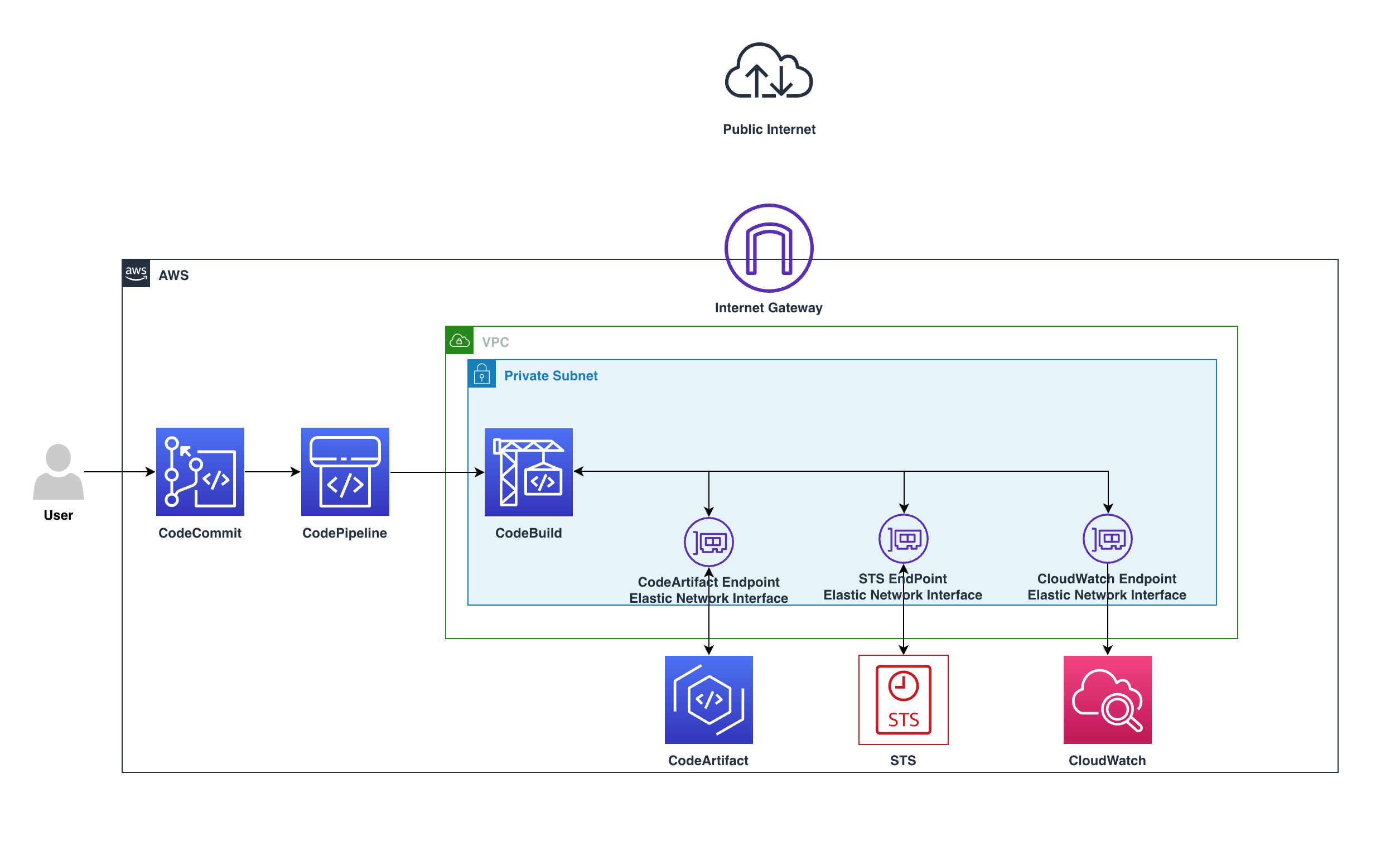
The diagram above shows how they remain private in the VPC and do not pass through the web gateway, going from CodeBuild via a private endpoint to the CodeArtifact service, all on a private subnet.
Requests will use the following VPC endpoints to connect to AWS services:
- CloudWatch Logs endpoint (for CodeBuild to place logs in CloudWatch);
- CodeArtifact endpoints
- AWS Security Token Service (AWS STS) endpoint
- Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) endpoint
Overview
- Create a CodeCommit repository:
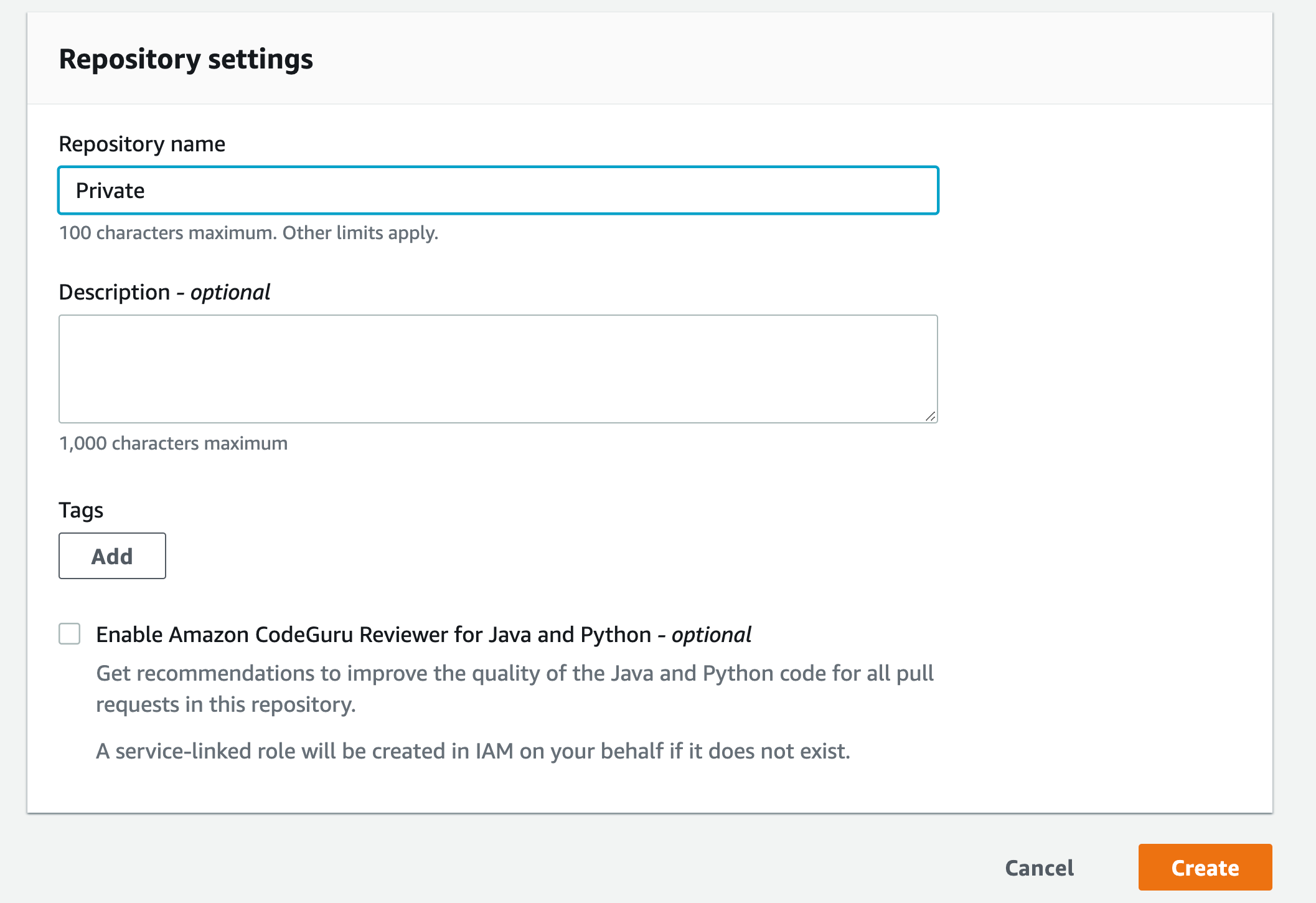
a) Go to the CodeCommit console, then click Create repository

b) Enter a name for the repository, then click Create
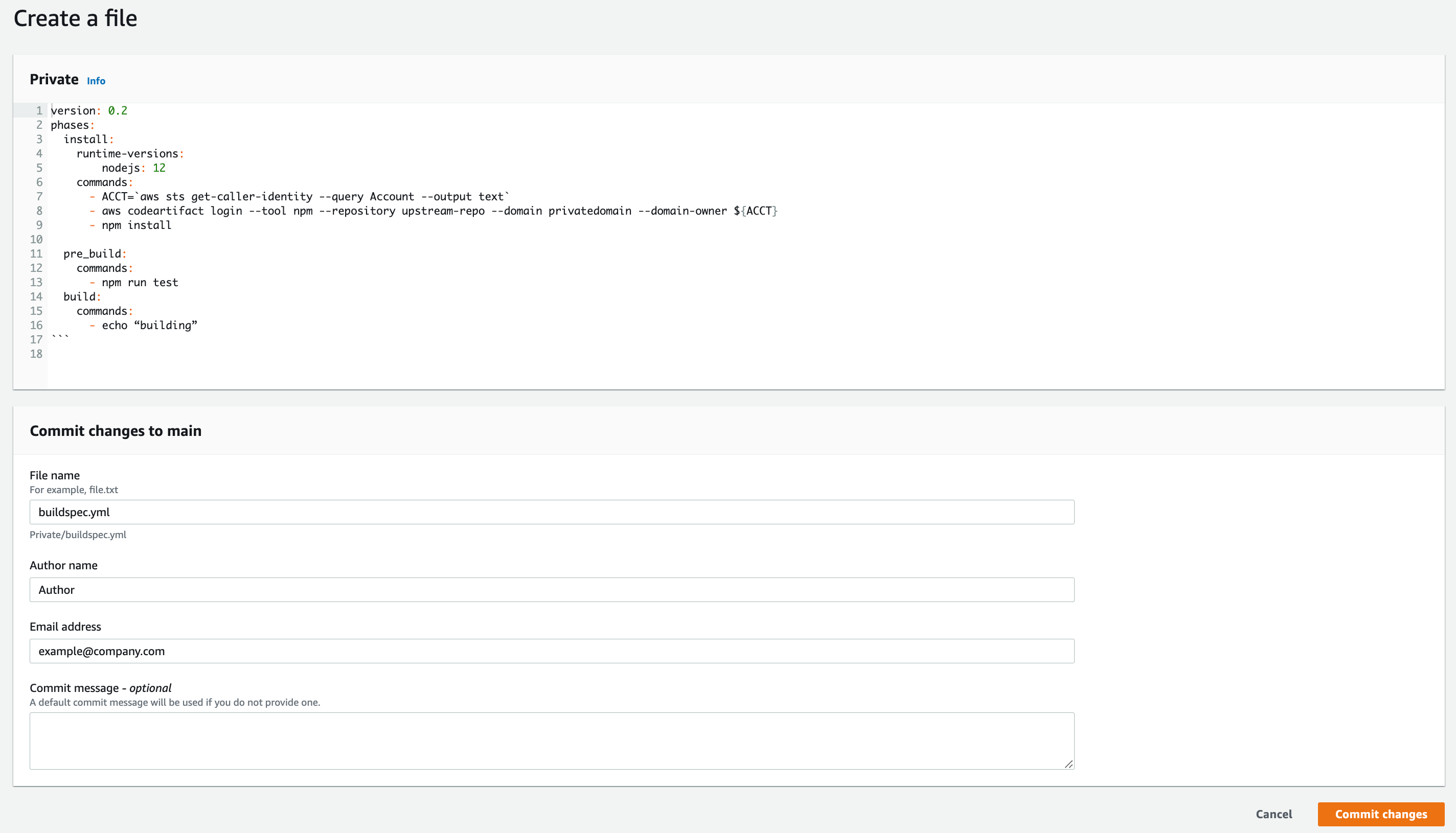
c) Scroll down and click Create file
d) Copy the example buildspec.yml file and paste it into the editor
Example buildspec.yml file:
e) Name the buildspec.yml file, enter your name and email address, then confirm the changes
2. Create a code artifact
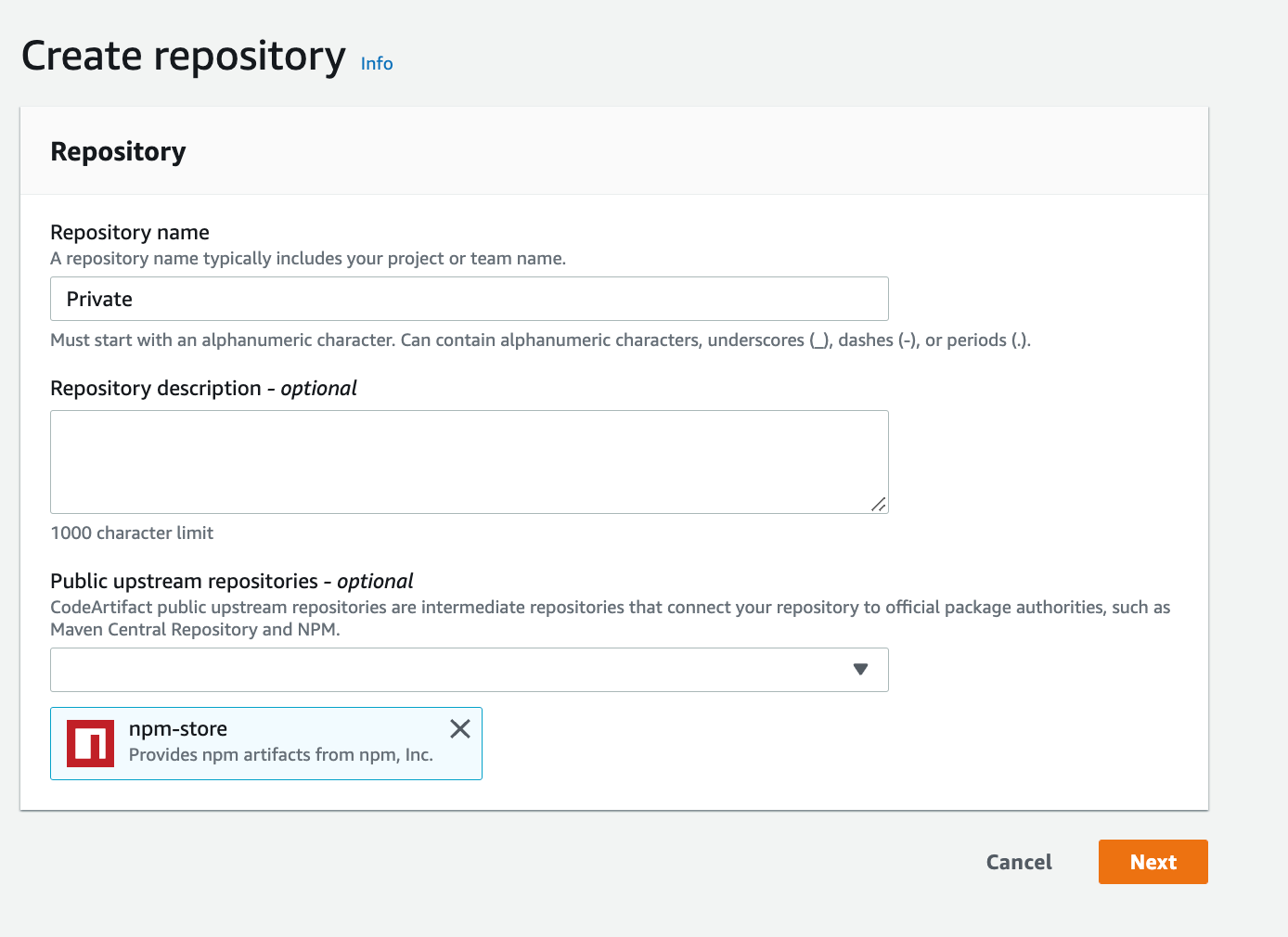
a) Go to the CodeArtifact console, then click Create repository
b) Give it a name and select npm-store as the public upsteam repository
c) For the domain, select this AWS account and enter the domain name
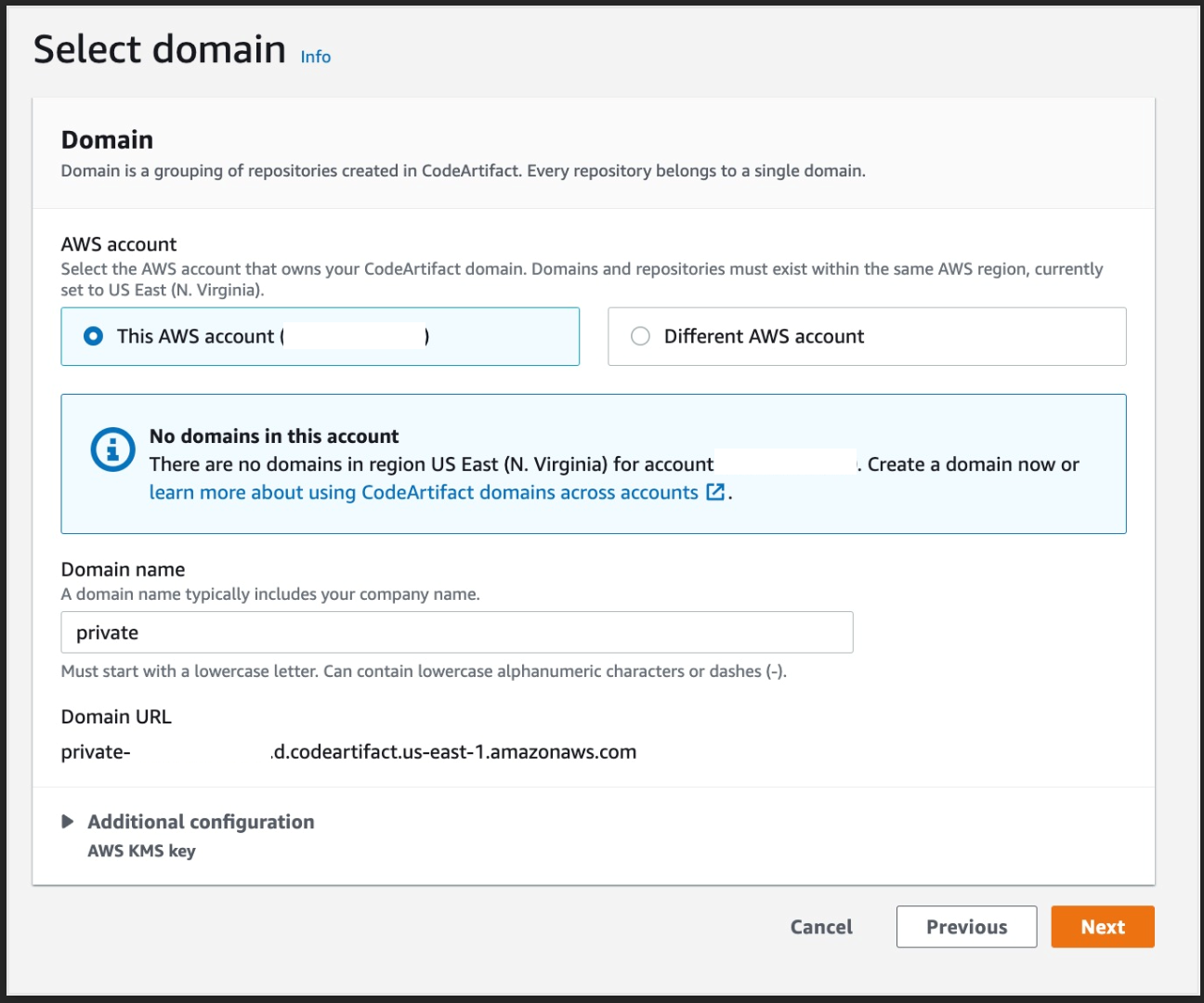
d) Click Next and then Create repository
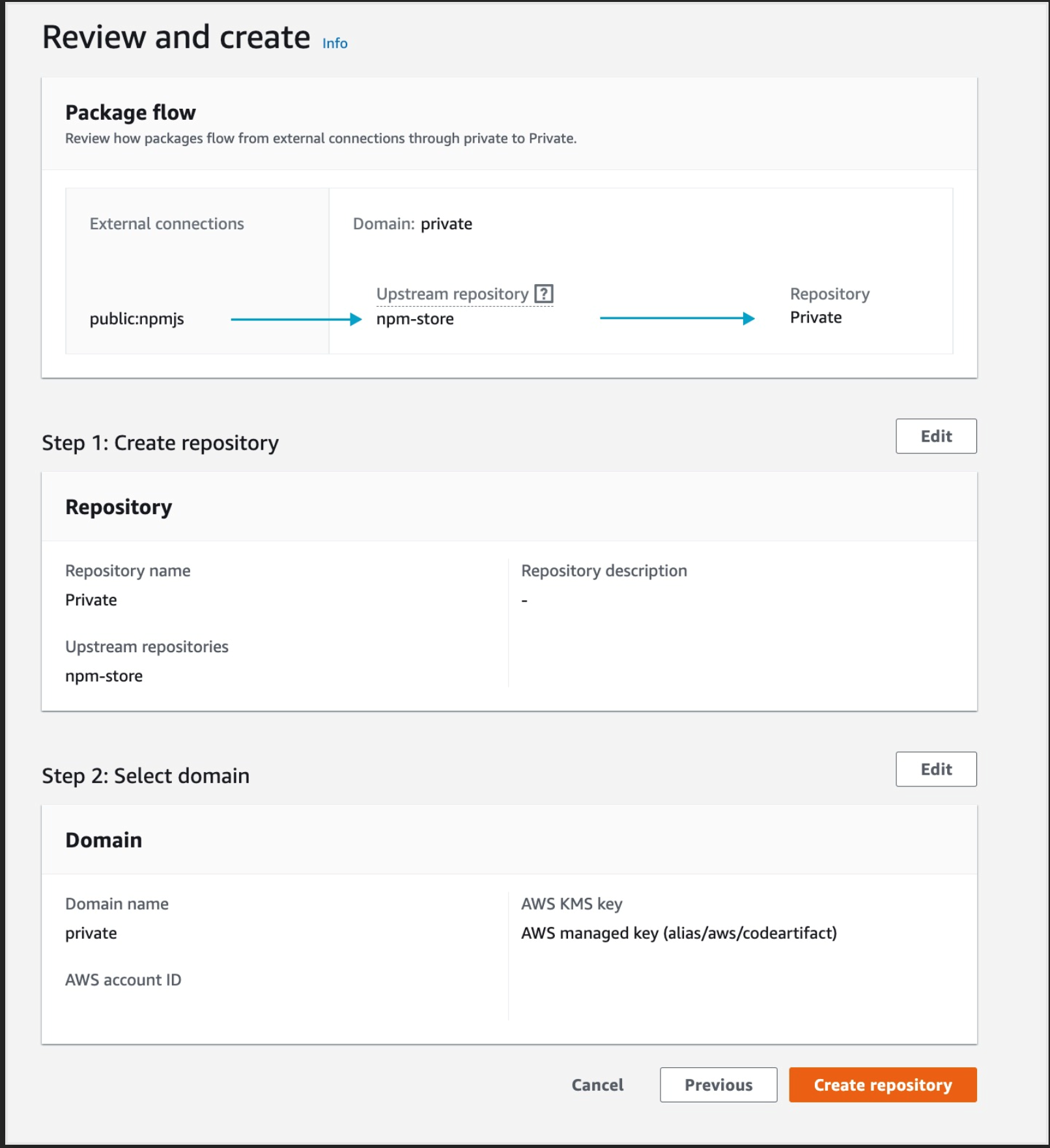
3. create a CI/CD using CodePipeline
a) Go to the CodePipeline console, then click Create a pipeline
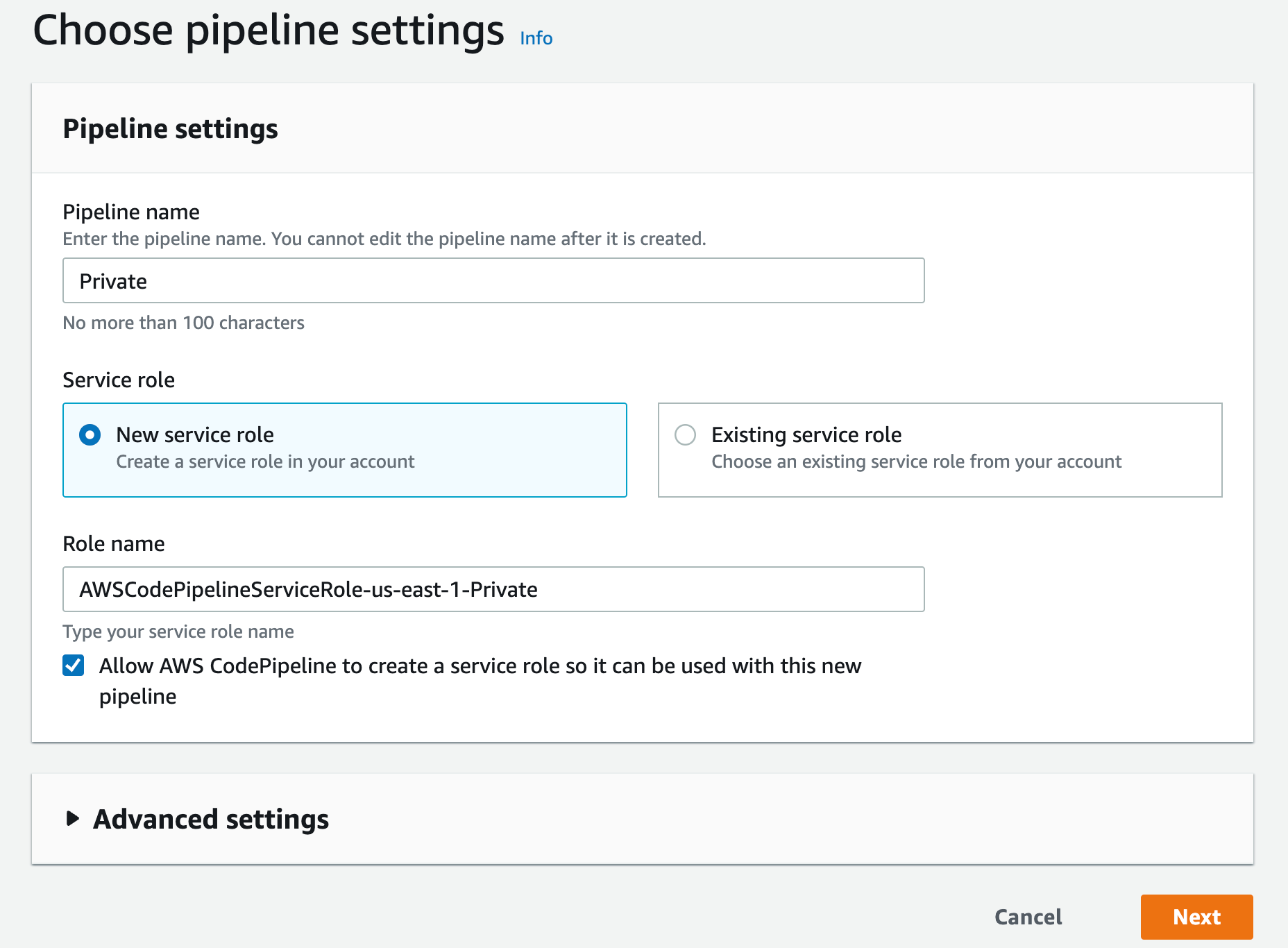
b) Enter a name, leave the service role as 'New service role' and click Next
c) Select AWS CodeCommit as the source provider
d) Then select the CodeCommit repository you created earlier; for the branch, select the main one and click Next
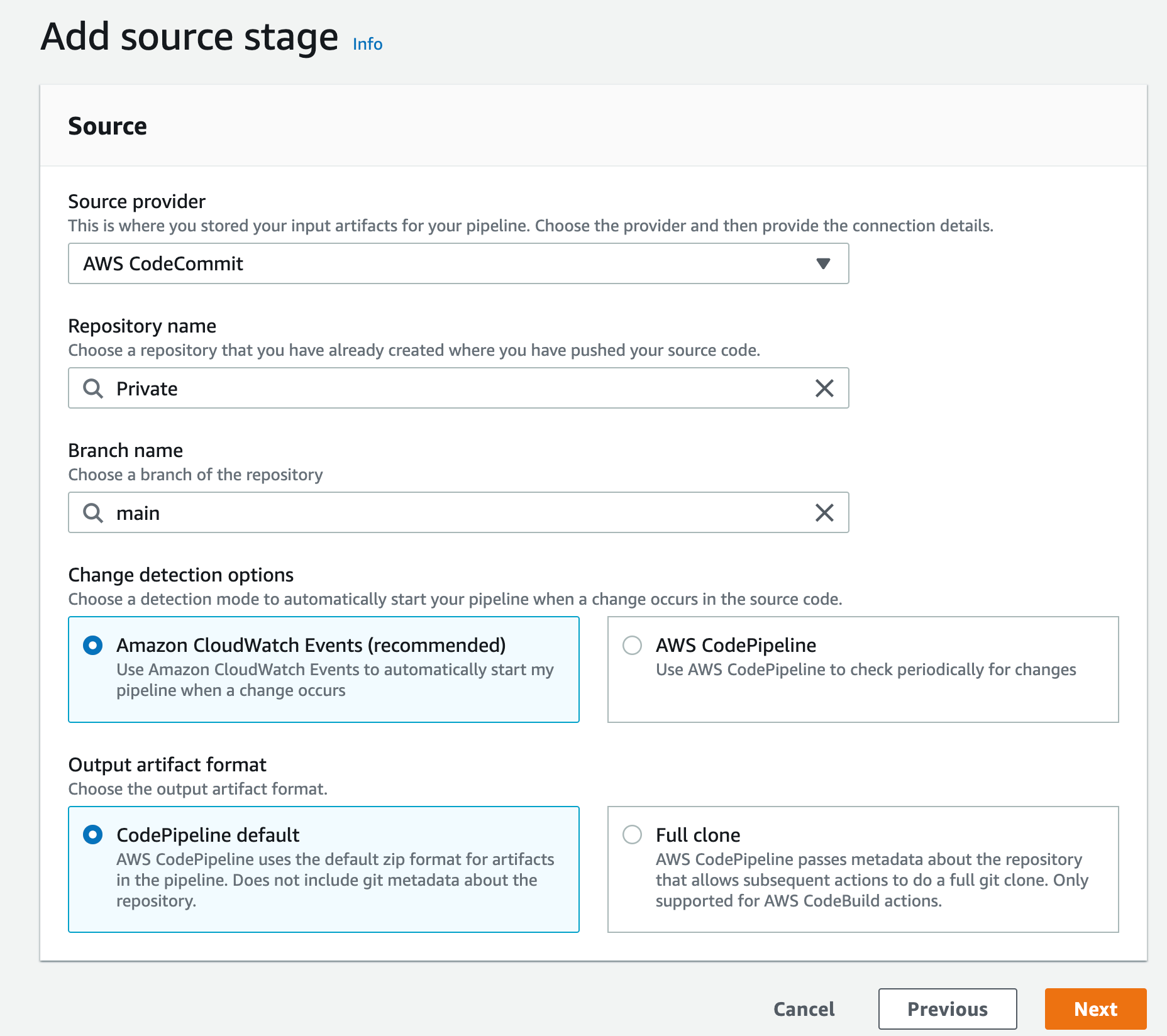
e) At the compile stage, select AWS CodeBuild as the compile provider and then click Create Project
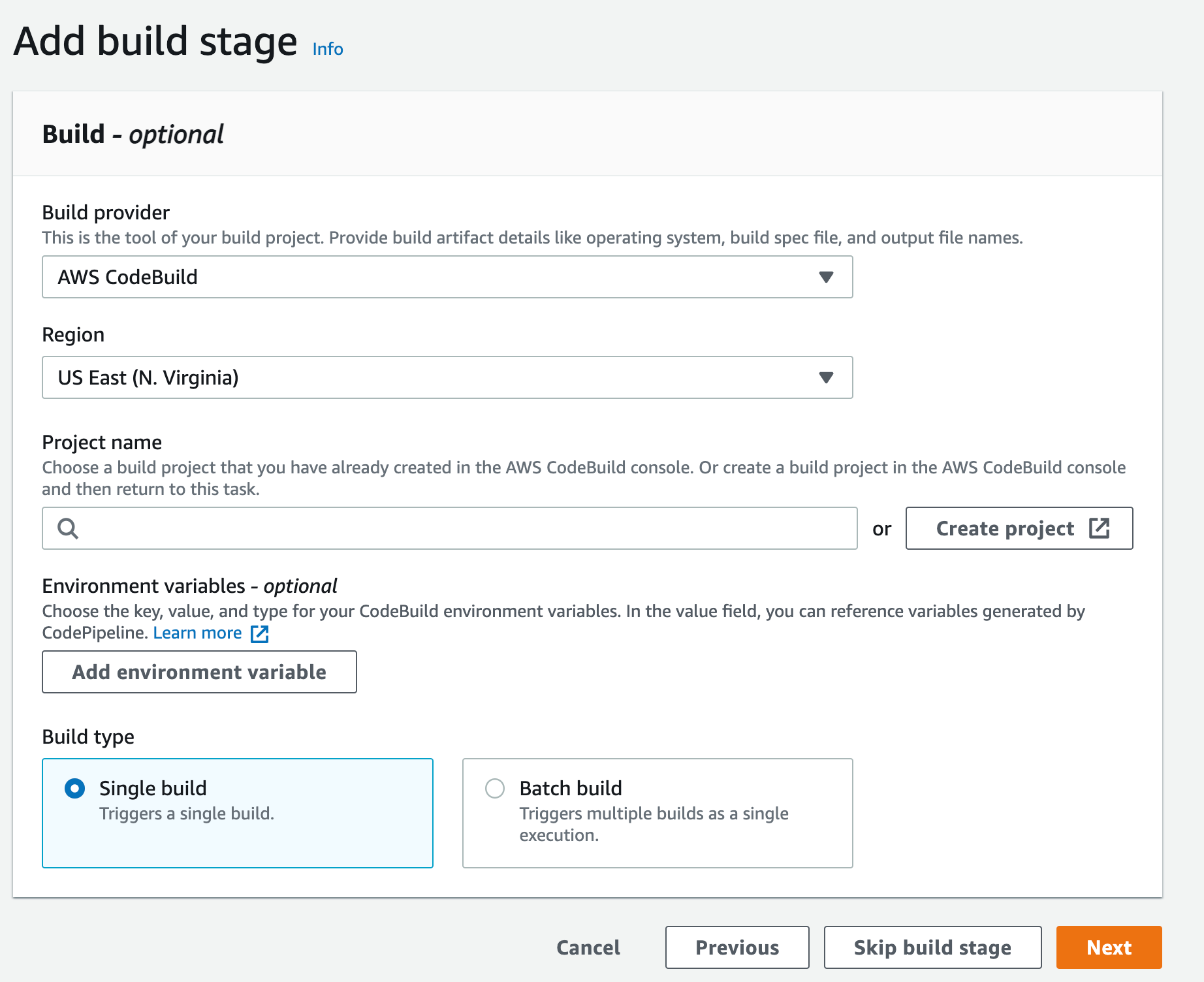
f) This will open a new window to create a new project. Give this project a name
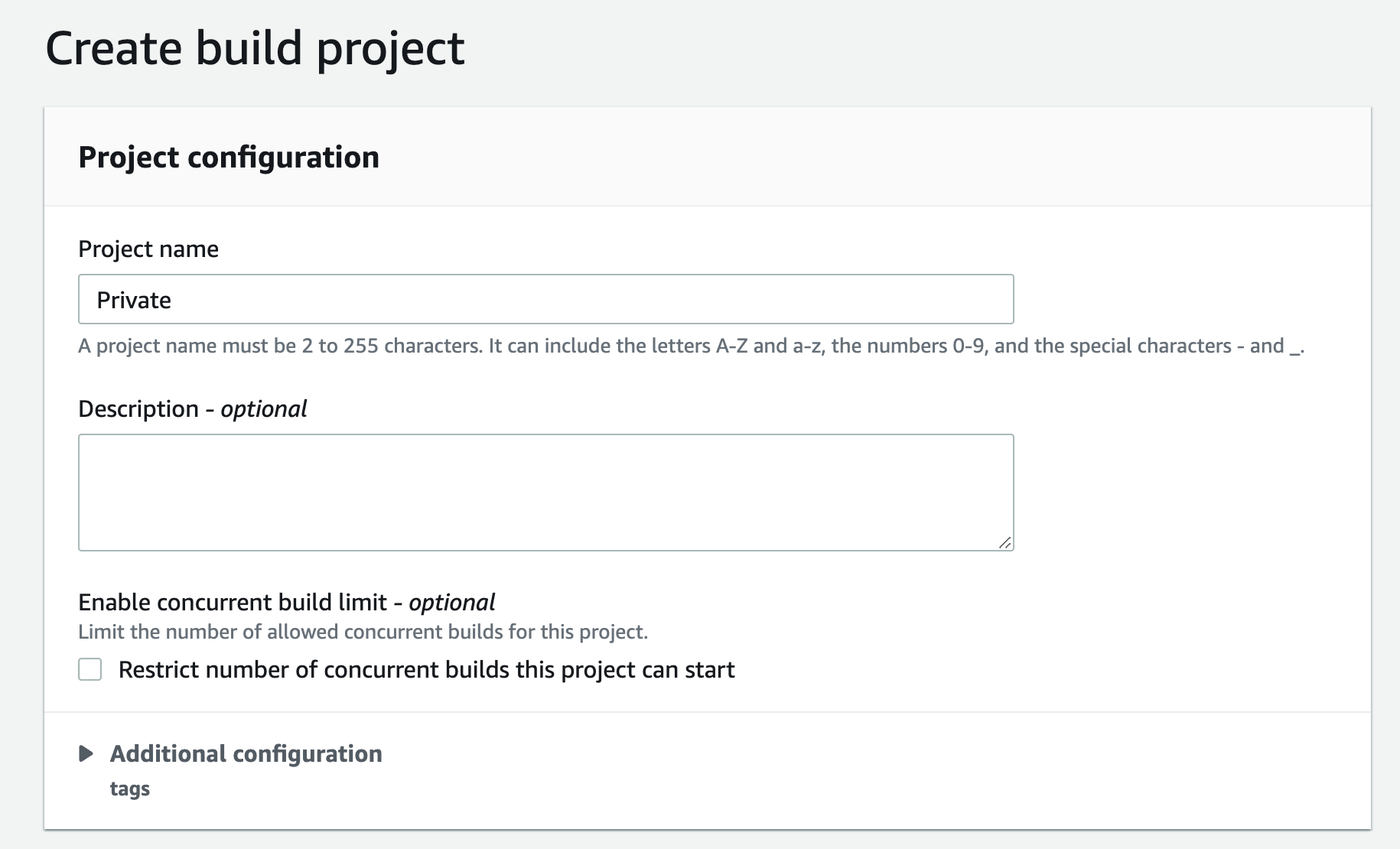
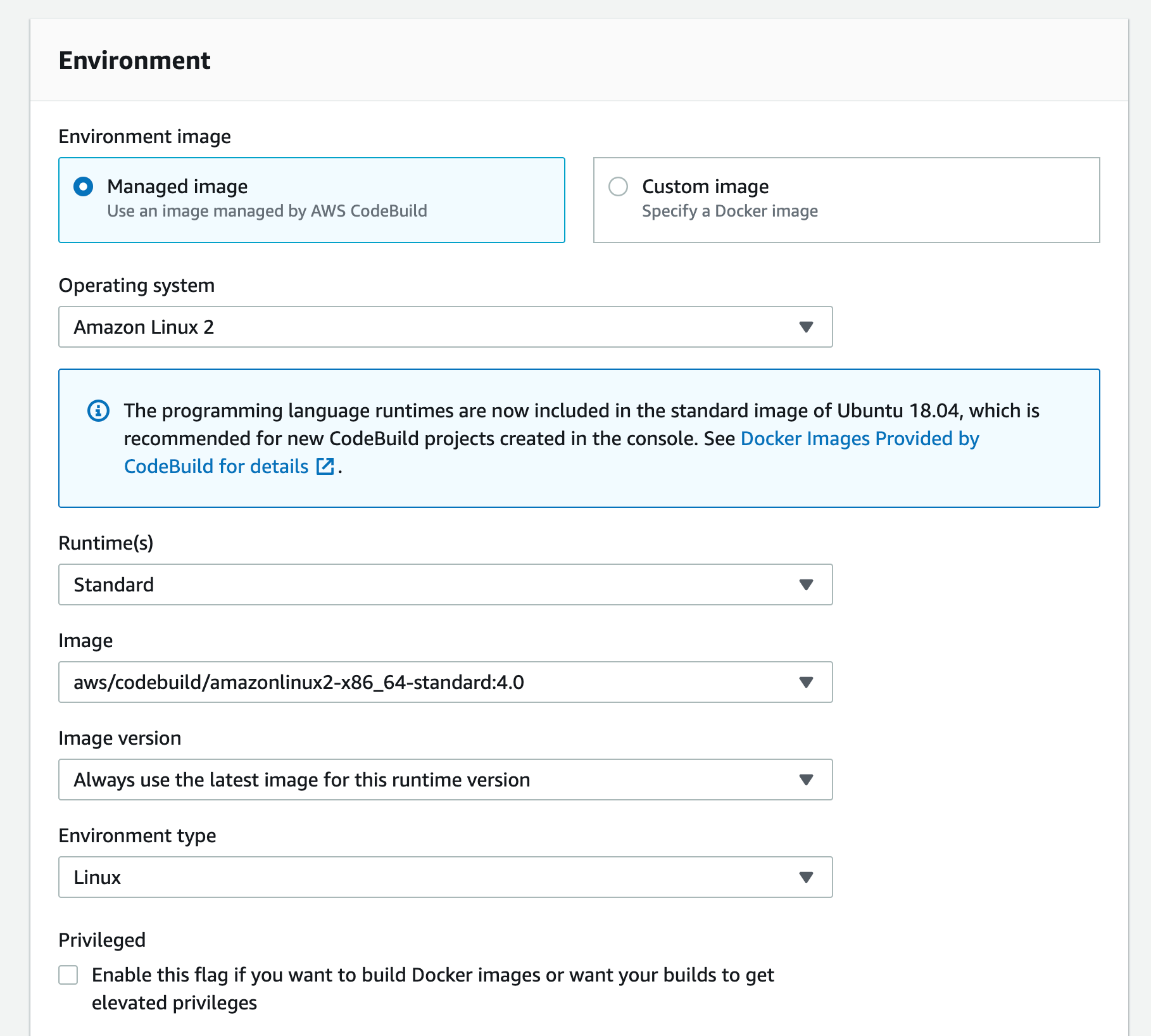
g) Scroll down to the Environment section: select Managed Image,
h) Under Operating System, select "Amazon Linux 2",
i) Run time "Standard"
j) For image, select aws/codebuild/amazonlinux2-x86+64-standard:4.0 For image version: always use the latest image for this version of the runtime environment
k) Select Linux for the environment type
l)Leave the Privileged option unchecked and set the Service Role to "New Service Role"
m) Expand Additional configurations and scroll down to the VPC section, select the desired VPC, its subnets (it is recommended to select multiple AZs to ensure high availability), and security group (security group rules must allow resources that will use the VPC endpoint to communicate with the AWS service to communicate with the endpoint's network interface, the default VPC security group will be used here as an example)
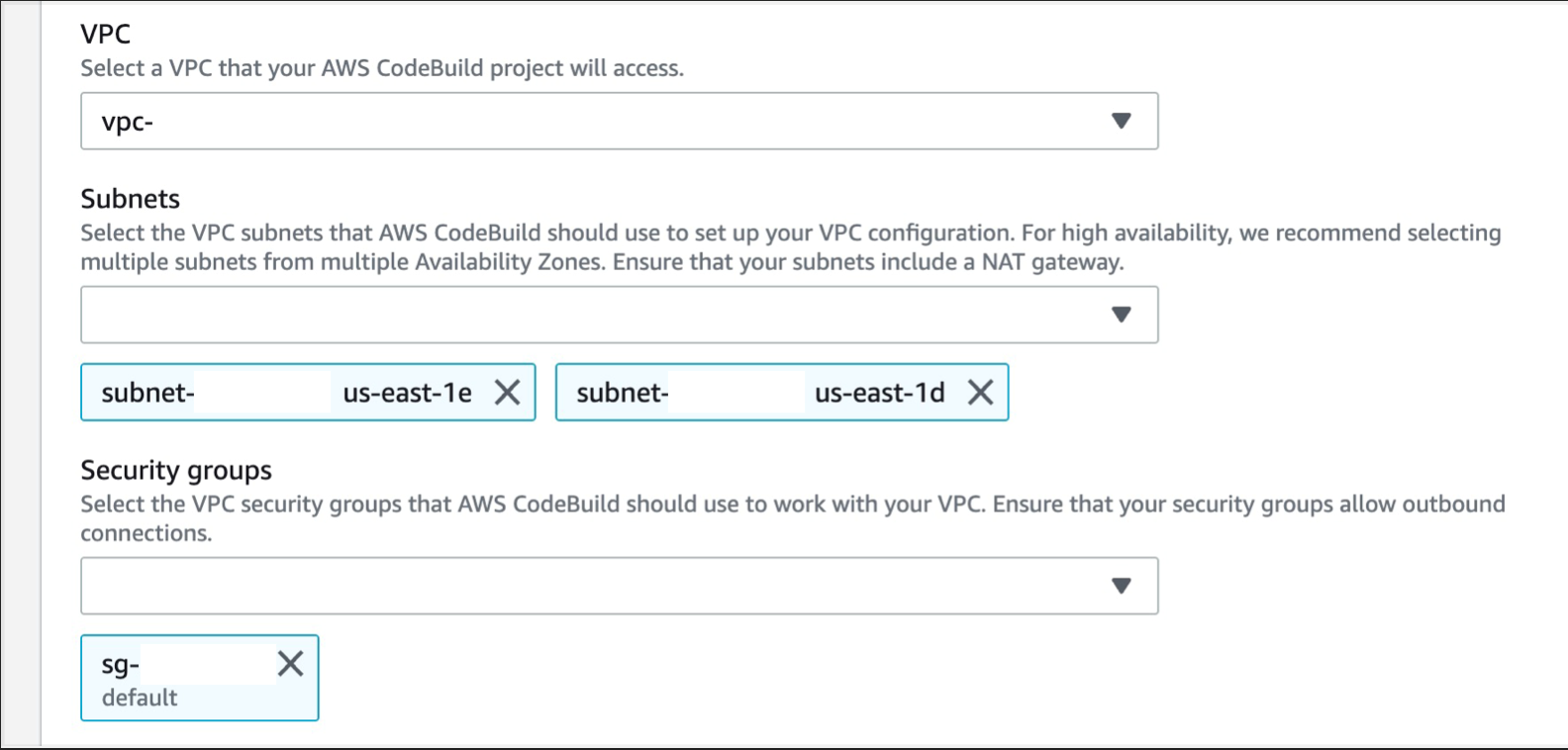
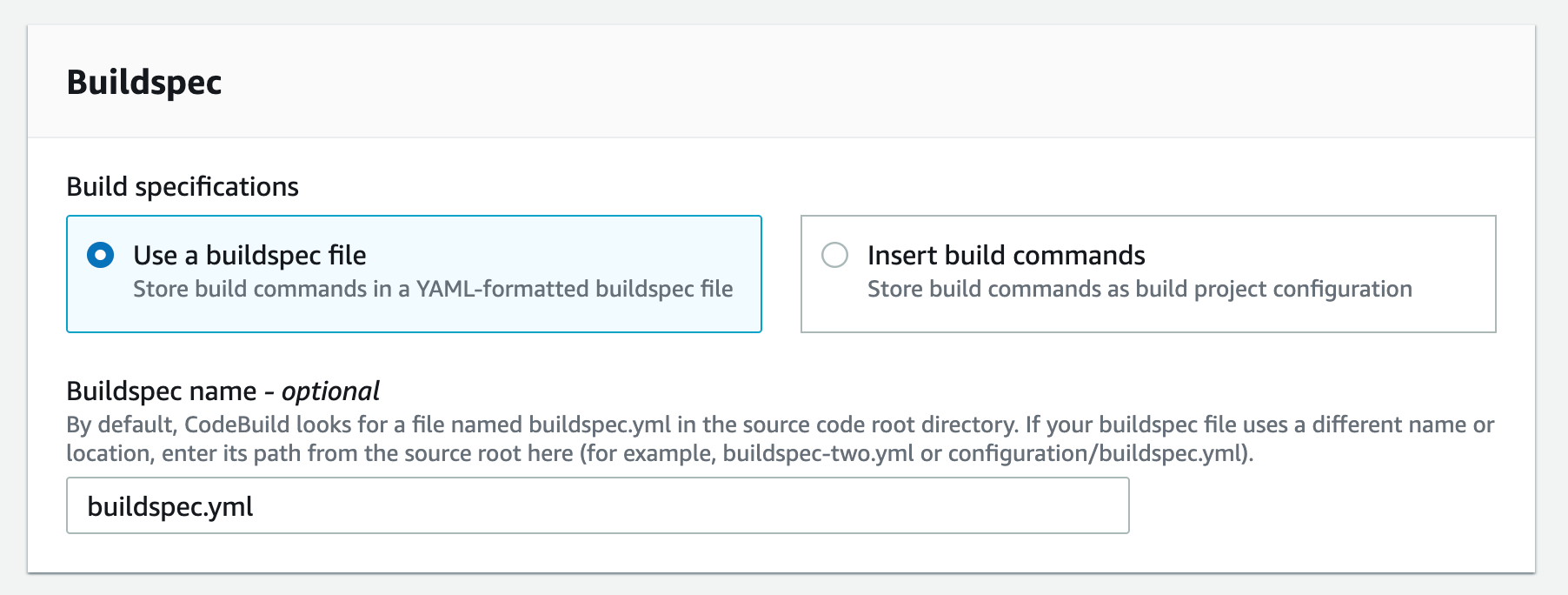
n) Scroll down to Buildspec, and select "Use buildspec file" and enter "buildspec.yml" as the Buildspec name
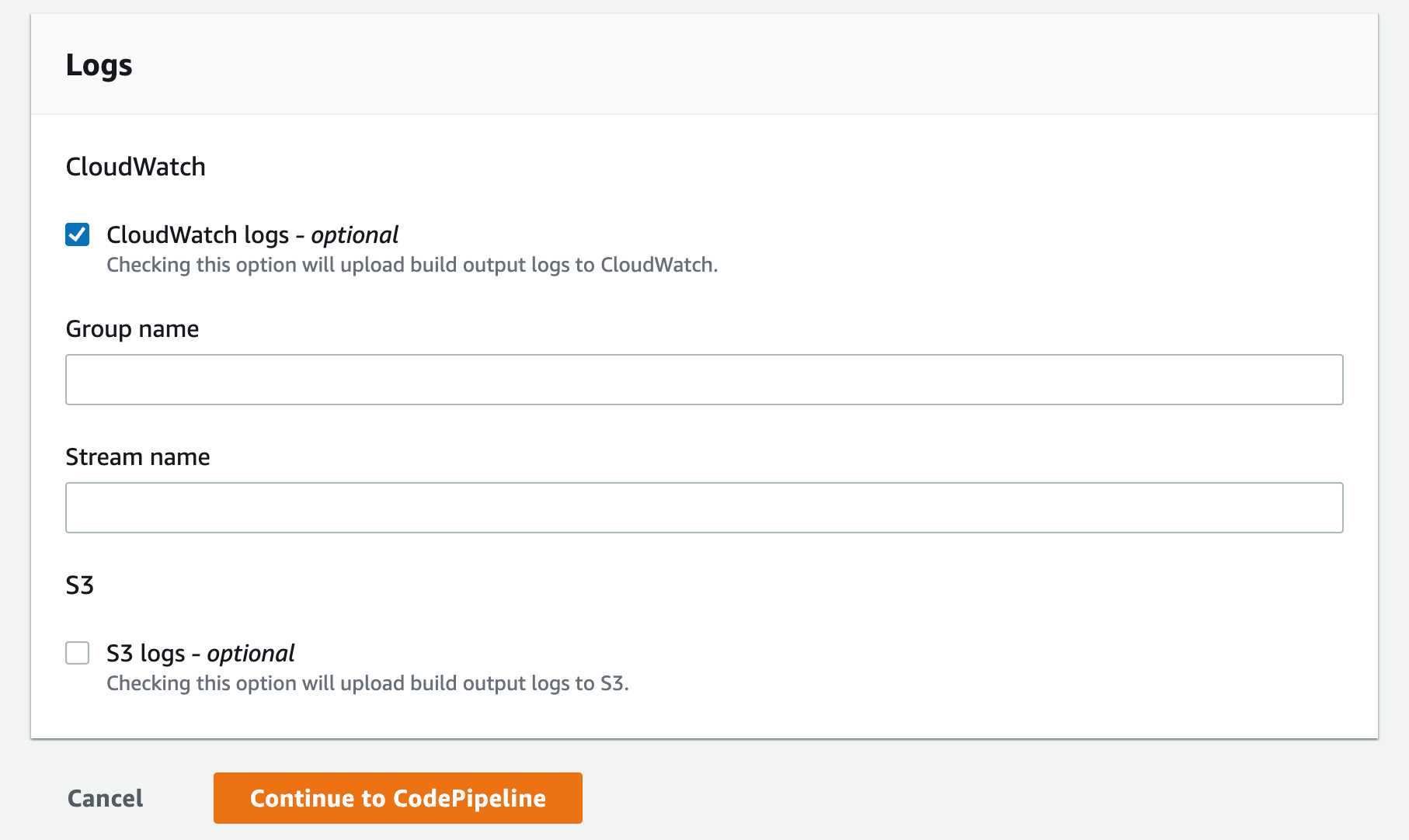
o) Select the CloudWatch logs option. You can leave the group name and stream blank, which will allow the service to use the default values and click Continue to CodePipeline
p) This will create a new CodeBuild project and update the CodePipeline page. You can now click Continue
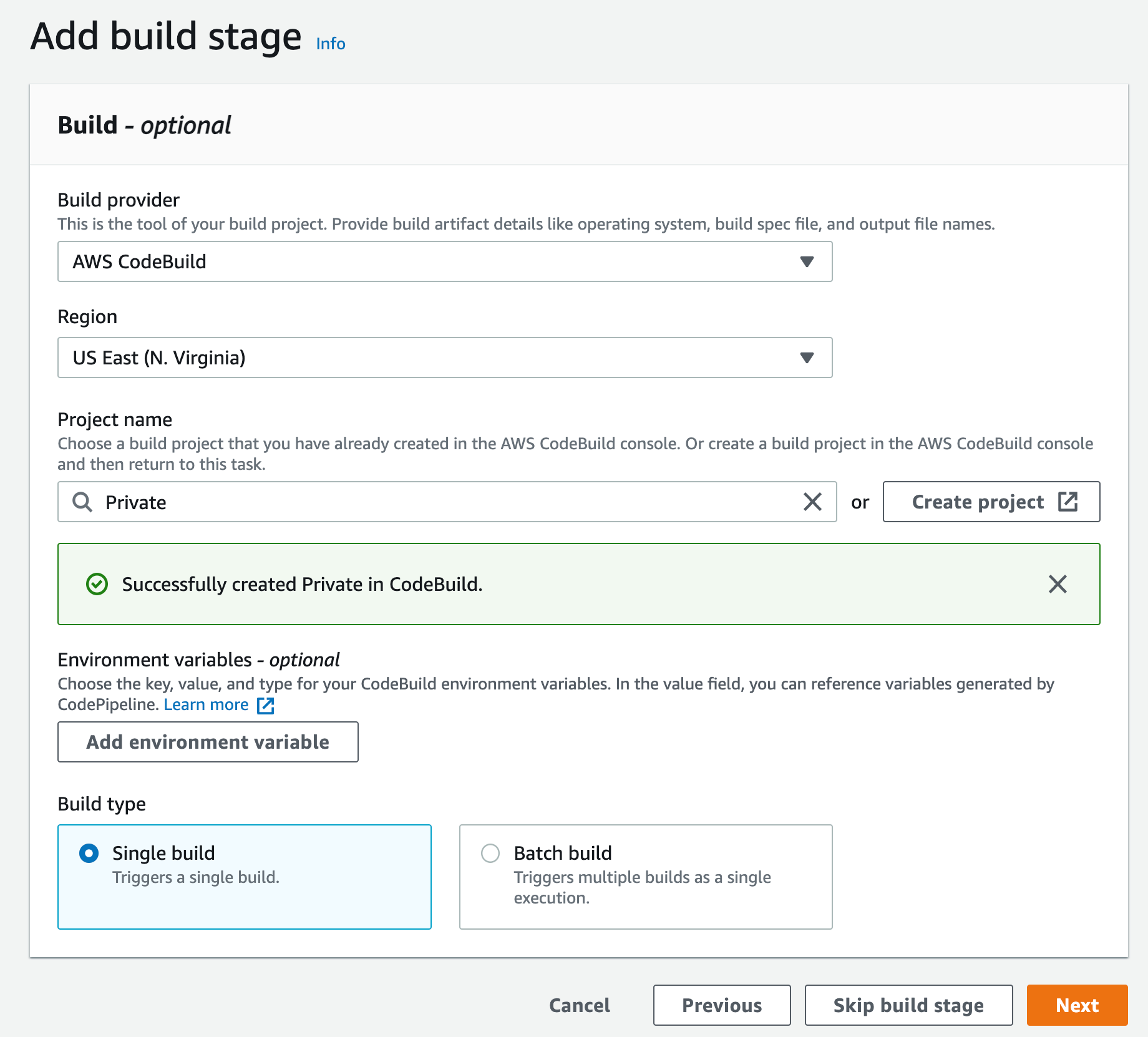
r) Since you are not deploying this to any environment, you can skip the deployment step and click Skip deployment step
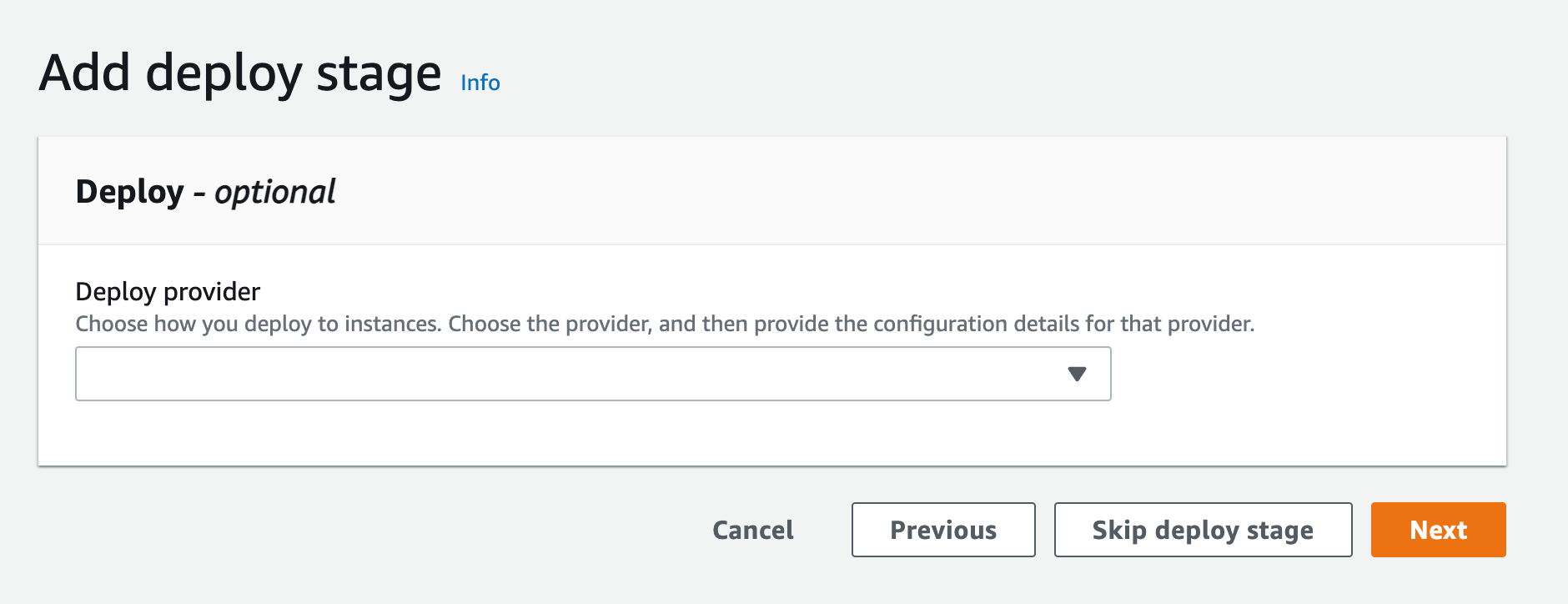
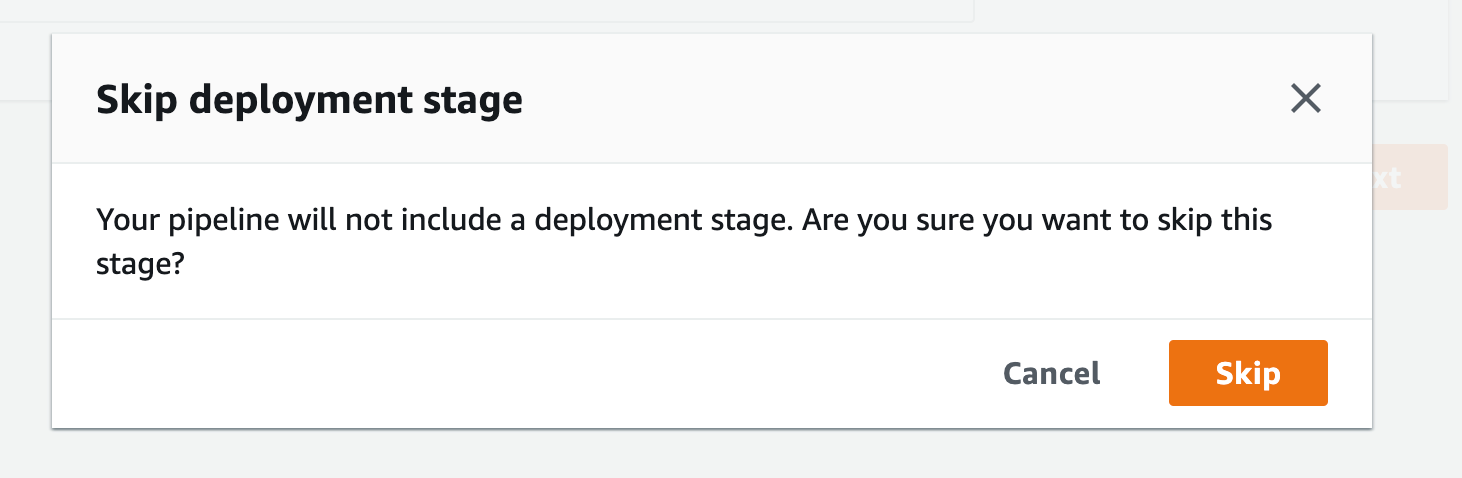
s) When the pop-up appears, click skip again, and you will see the review page. Scroll to the end and click Create pipeline
4. Create a VPC endpoint for Amazon CloudWatch logs. This will enable CodeBuild to send execution logs to CloudWatch:
a) Go to the VPC console and select "Endpoints" from the navigation menu on the left.
b) Click Create Endpoint.

c) Select "AWS Services" as the service category. You can set the name of the new endpoint and make sure you use something descriptive.
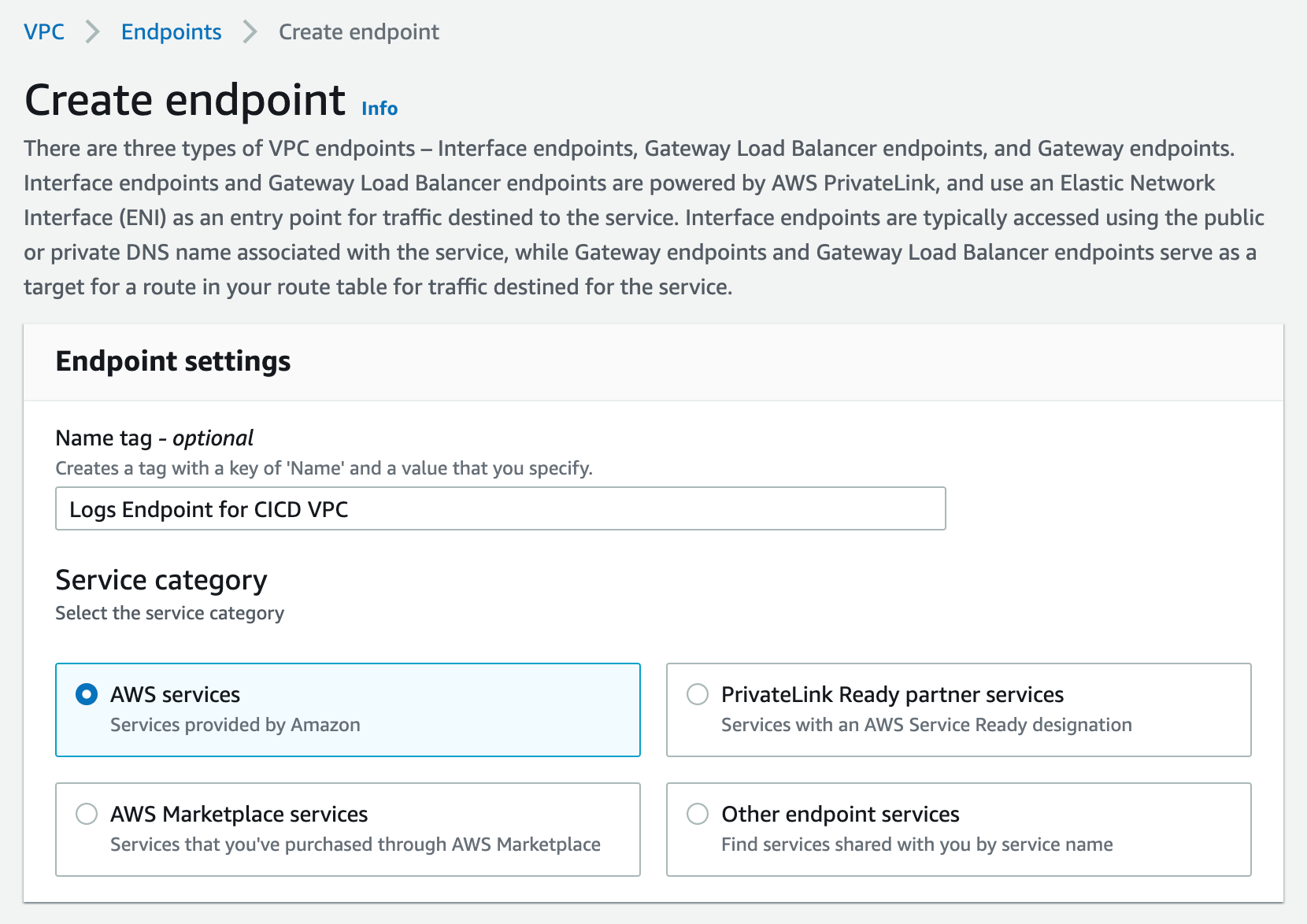
d) From the list of services, search for the endpoint by typing logs in the search bar and selecting the one from com.amazonaws.us-west-2.logs.This guide can be done in any region that supports services. You will be using the us-west-2 service; select the appropriate area for your workload.
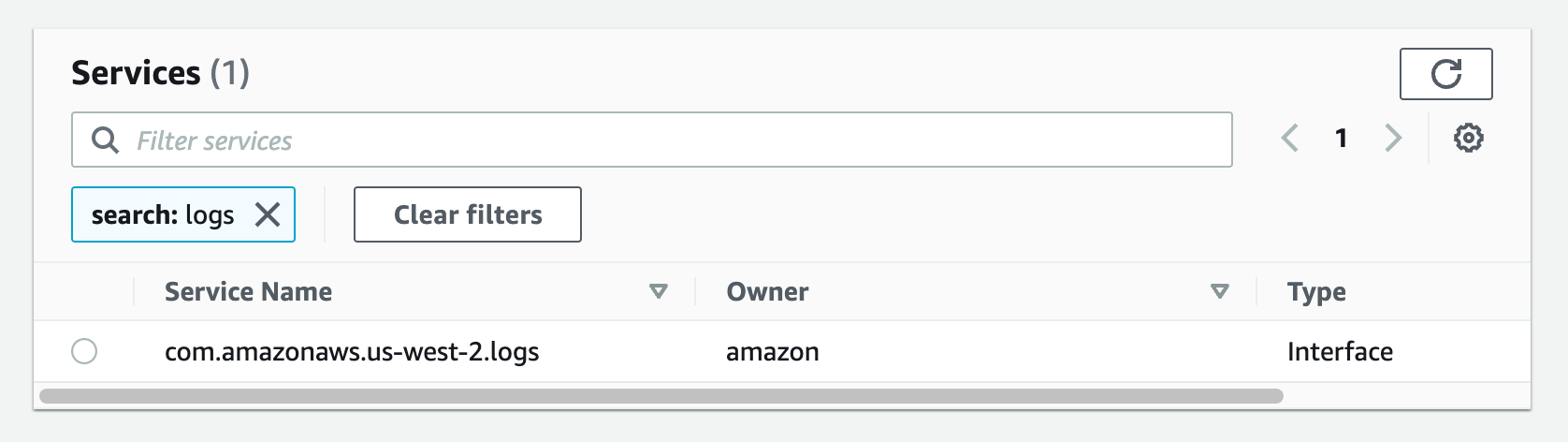
e) Select the VPC with which you want to associate the endpoint and ensure that the Enable DNS name option is checked in the additional settings.
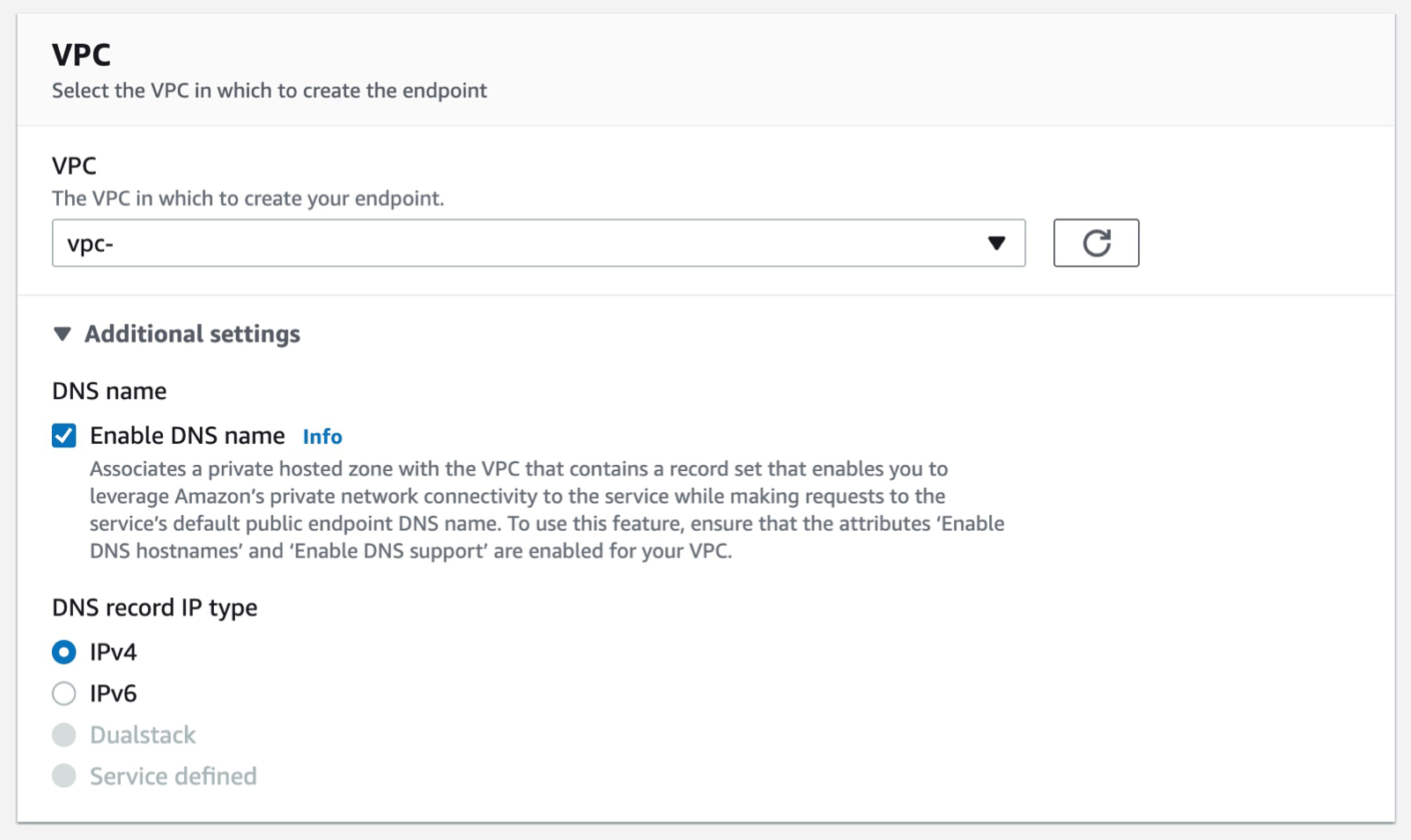
f) Select the subnets you want to associate the endpoint with and you can leave the security group as default and the policy as blank.
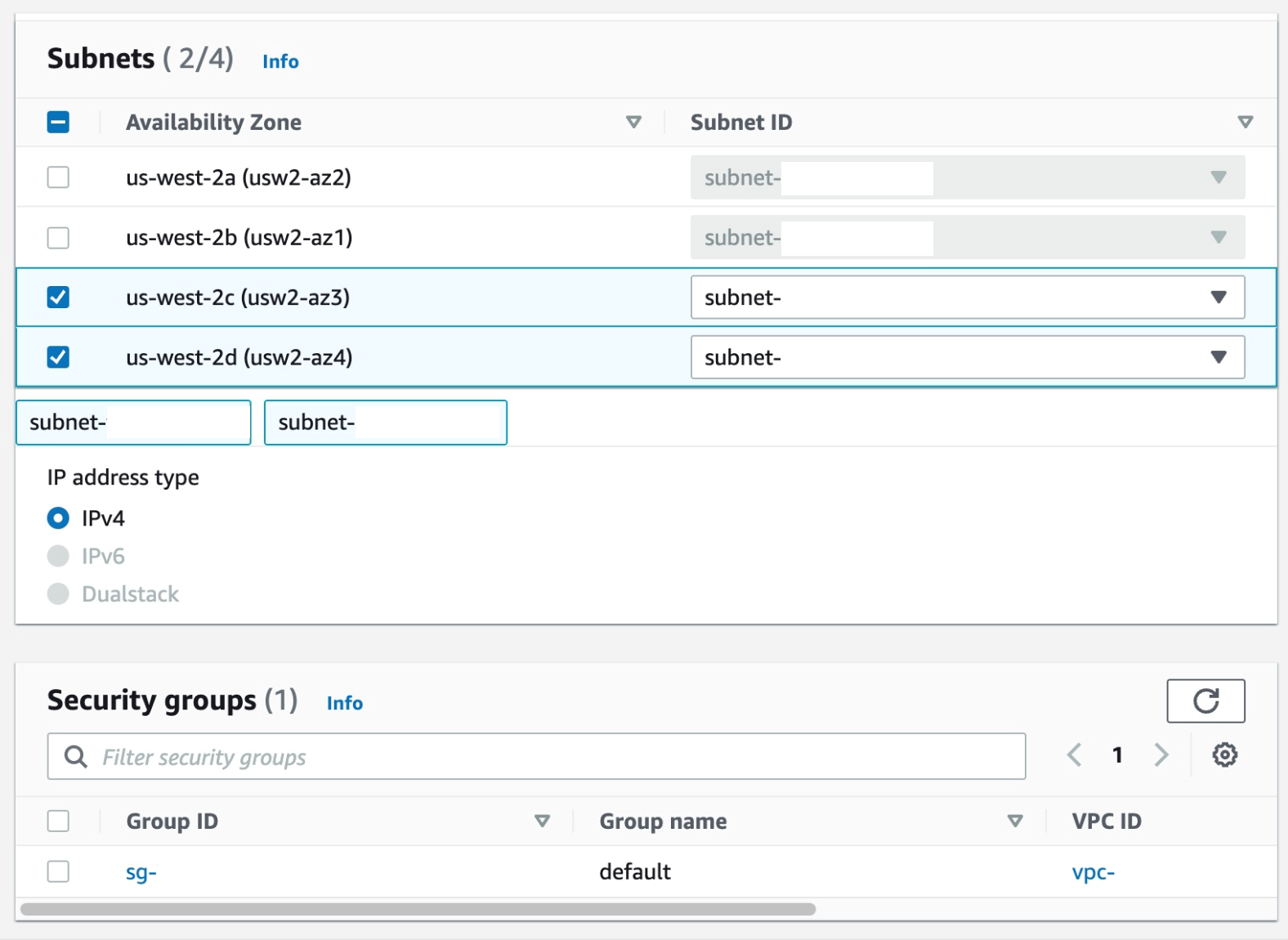
g) Select Create endpoint.
 5. Create a VPC endpoint for CodeArtifact. When writing this article, CodeArifact has two endpoints: one is for API operations, such as service-level operations and authentication, and the other is for using a service, such as downloading modules for our code. You will need both endpoints to automate your work with CodeArtifact. Therefore, you will create both endpoints with DNS enabled.
5. Create a VPC endpoint for CodeArtifact. When writing this article, CodeArifact has two endpoints: one is for API operations, such as service-level operations and authentication, and the other is for using a service, such as downloading modules for our code. You will need both endpoints to automate your work with CodeArtifact. Therefore, you will create both endpoints with DNS enabled.
Additionally, you will need an AWS Security Token Service (AWS STS) endpoint to call the get-caller-identity API:
Follow steps a-c from the steps used to create the log endpoint above.
a) From the list of services, you can search for the endpoint by typing codeartifact in the search bar and selecting the one from com.amazonaws.us-west-2.codeartifact.api.
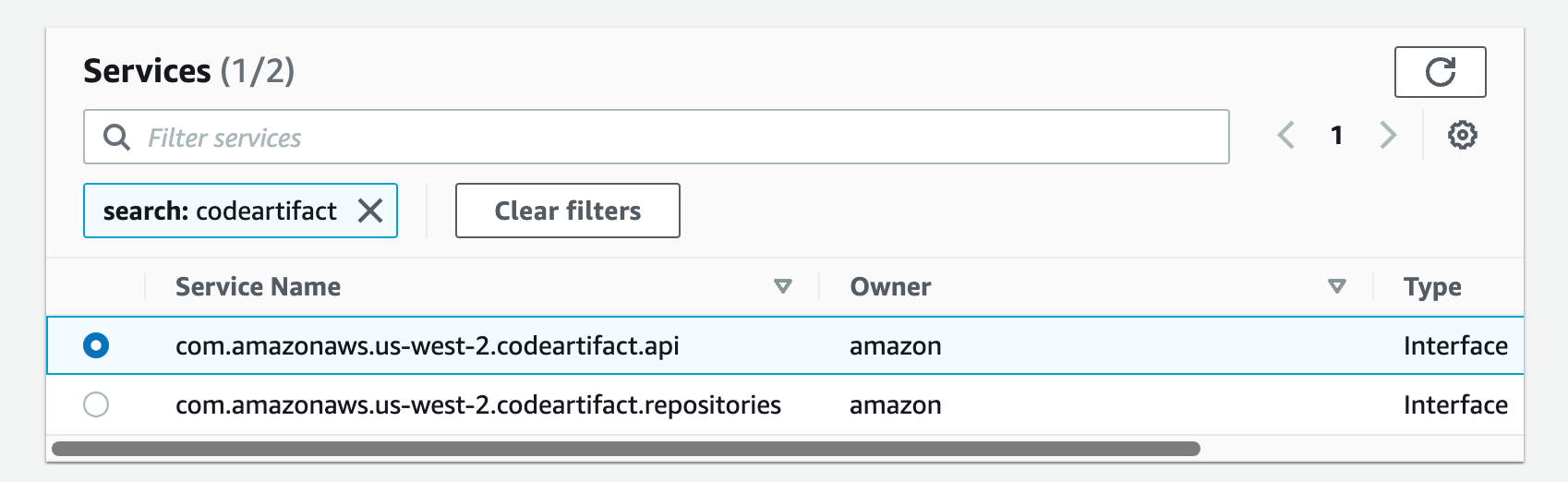
Follow steps e-g from part 4.
Then repeat the same for the com.amazon.aws.us-west-2.codeartifact.repositories service.
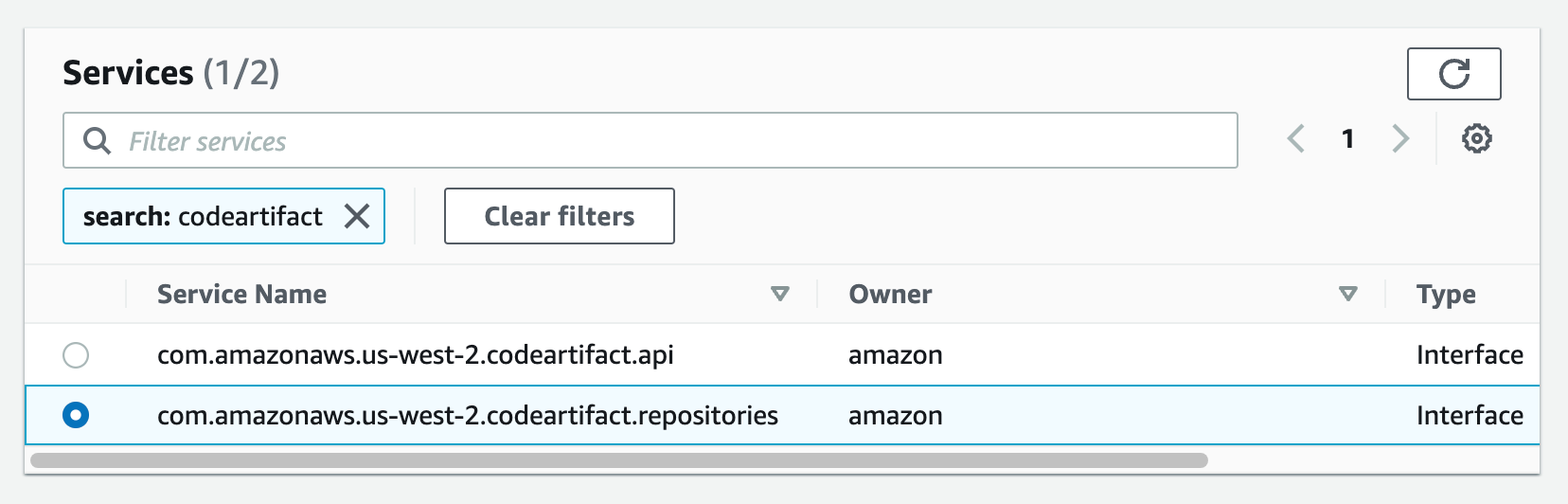
6. Enable the VPC endpoint for AWS STS:
Follow steps a-c from part 4
a) From the list of services, you can search for an endpoint by typing sts in the search bar and selecting the one from com.amazonaws.us-west-2.sts.
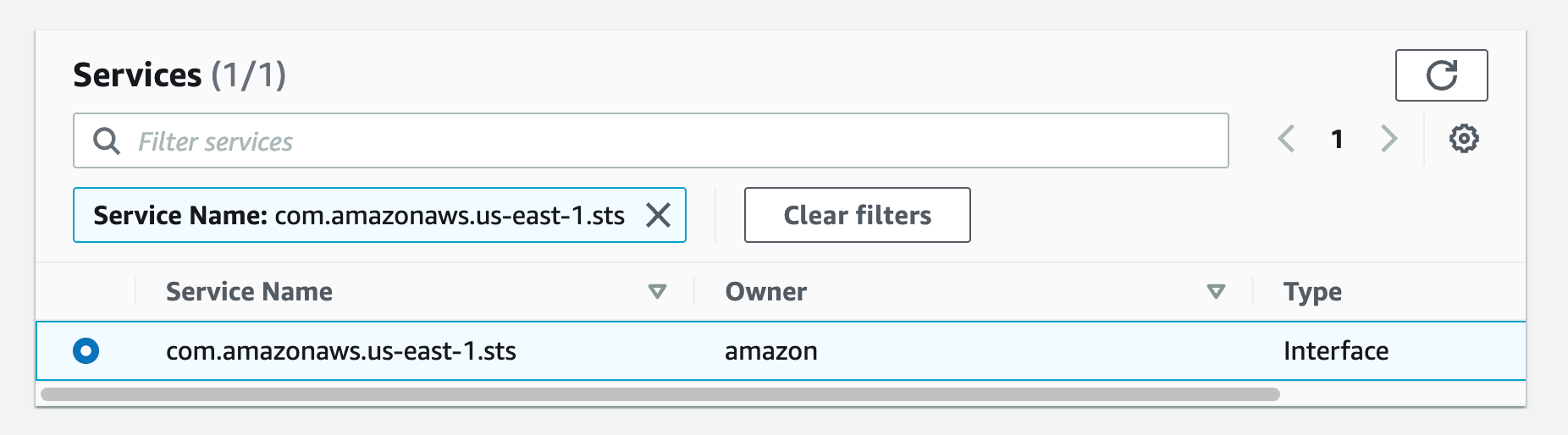
Then follow steps e-g from part 4.
- Create a VPC endpoint for S3:
Follow steps a-c from part 4
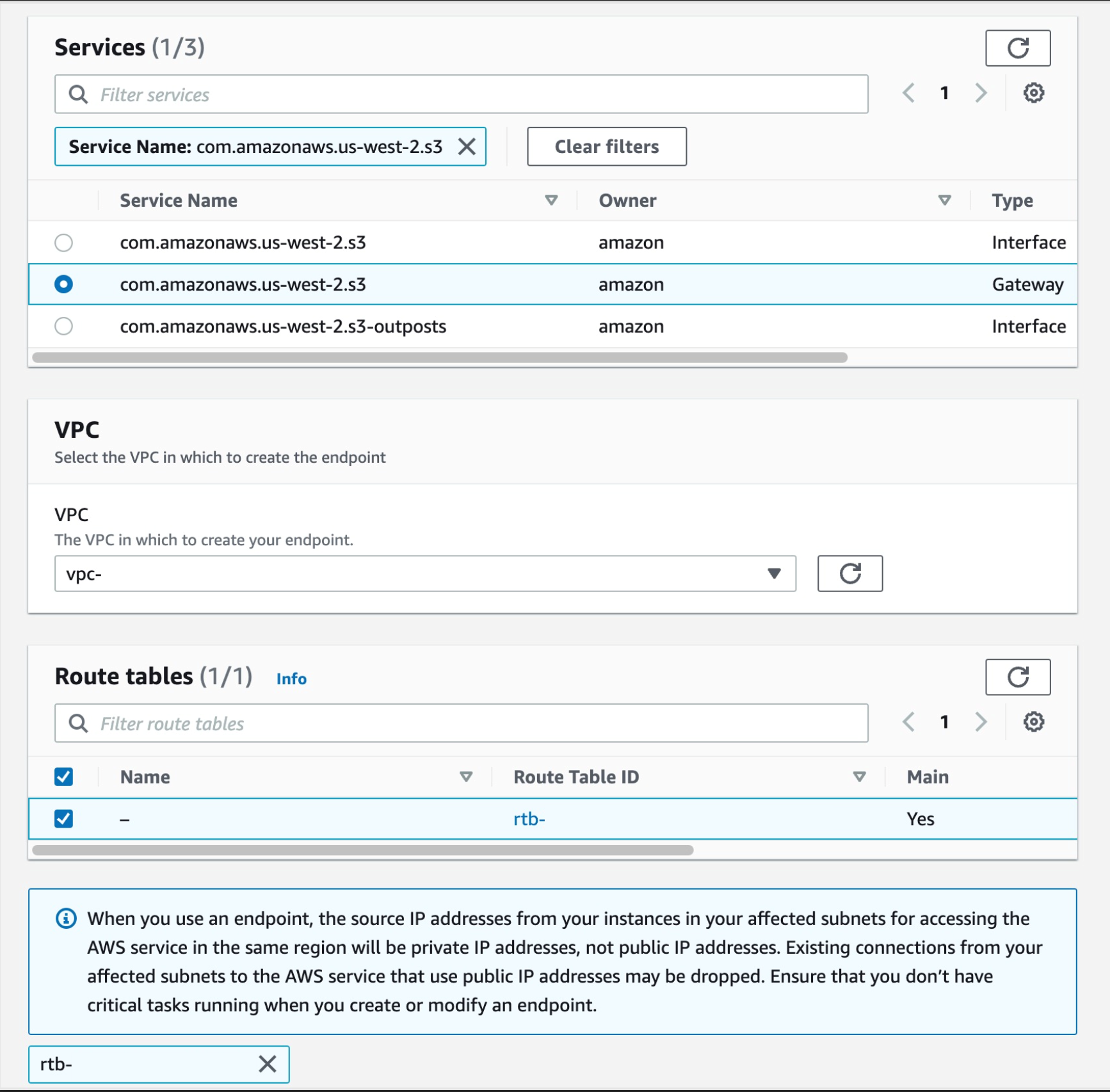
a) From the list of services, you can search for an endpoint by typing sts in the search bar and selecting the one from com.amazonaws.us-west-2.s3; choose the one with the Gateway type
Then, select your VPC and choose the routing tables for your subnets. This will automatically update the route table with the new S3.
8 . Now that we have all the endpoints set up, the final step is to update the pipeline to point to the CodeArtifact repository when downloading code dependencies. I will use CodeBuild buildspec.yml as an example.
Ensure that your CodeBuild AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) role has permission to perform STS and CodeArtifact actions.
Go to the IAM console and click Roles in the navigation menu on the left-hand side, then search for the name of your IAM role, in your case, because you selected the 'New service role' option in step 2.k it was created with the name 'codebuild-Private-service-role' (codebuild--service-role)
In the Add permissions menu, click Create built-in rules
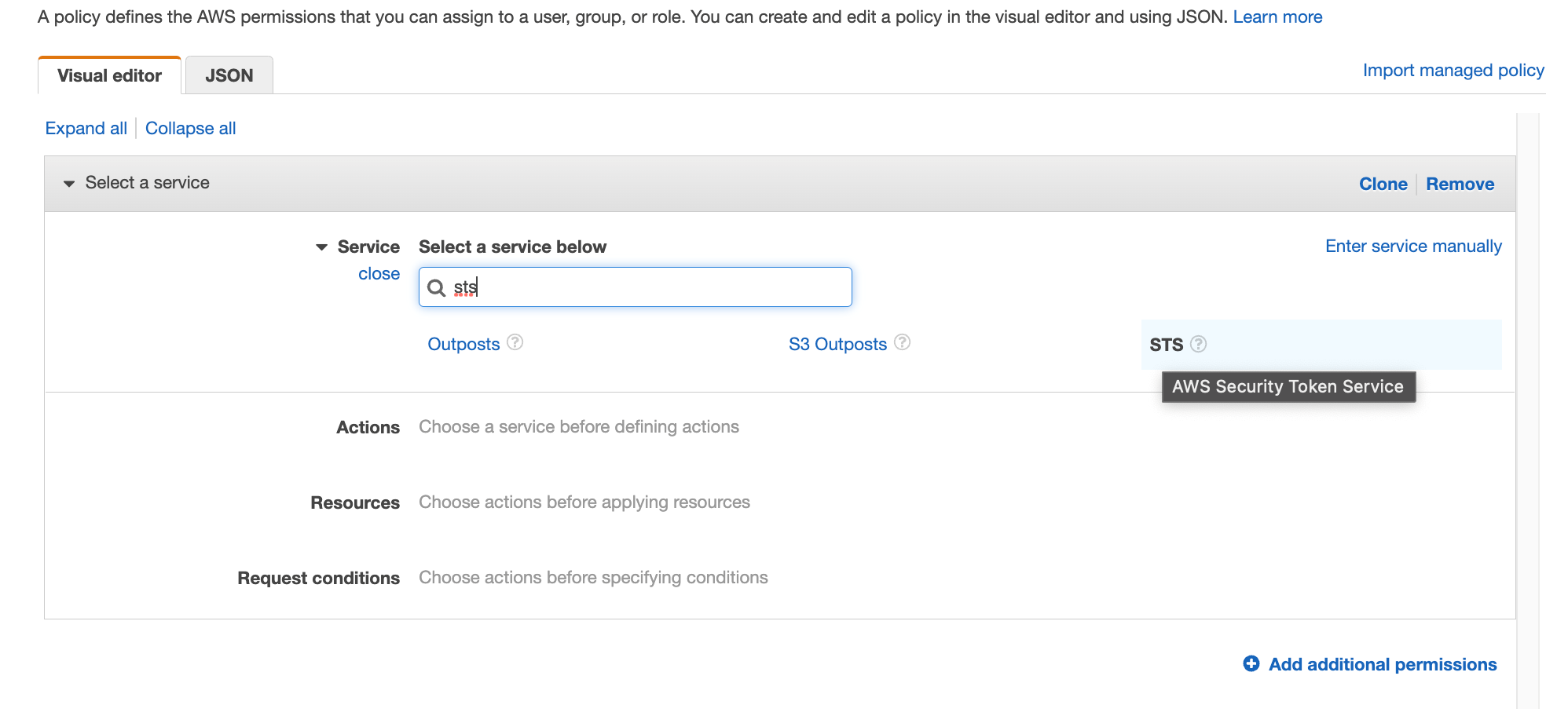
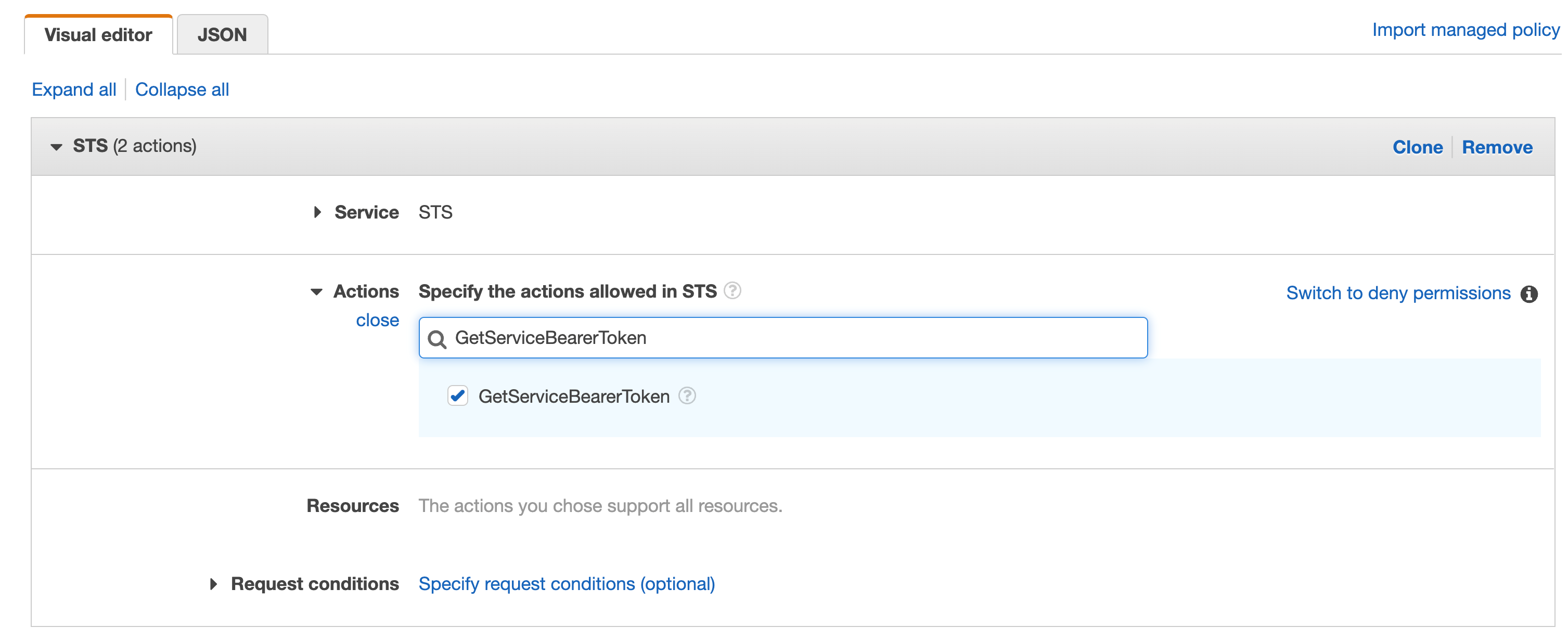
Search for STS in services, then select STS
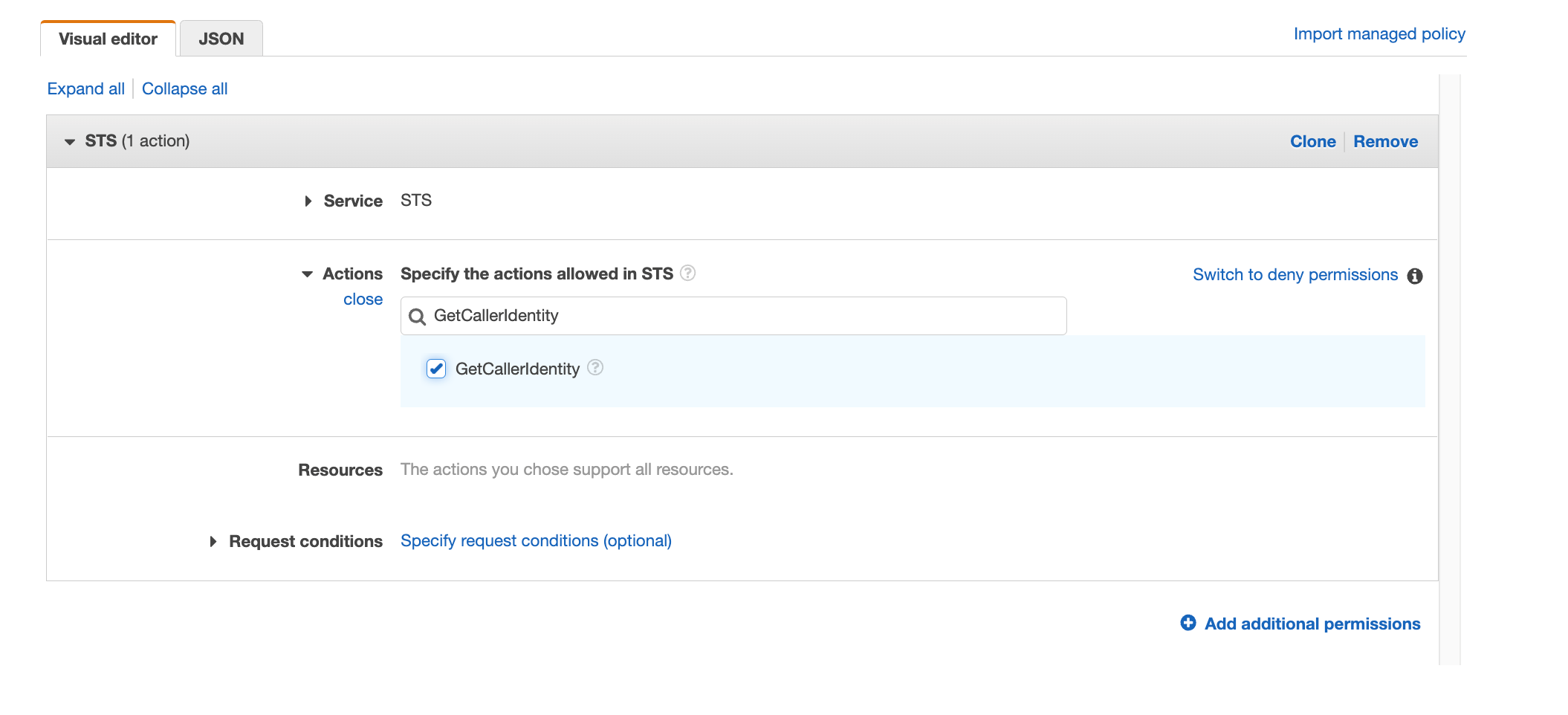
Search for "GetCallerIdentity" and select the action
Repeat the same with "GetServiceBearerToken"
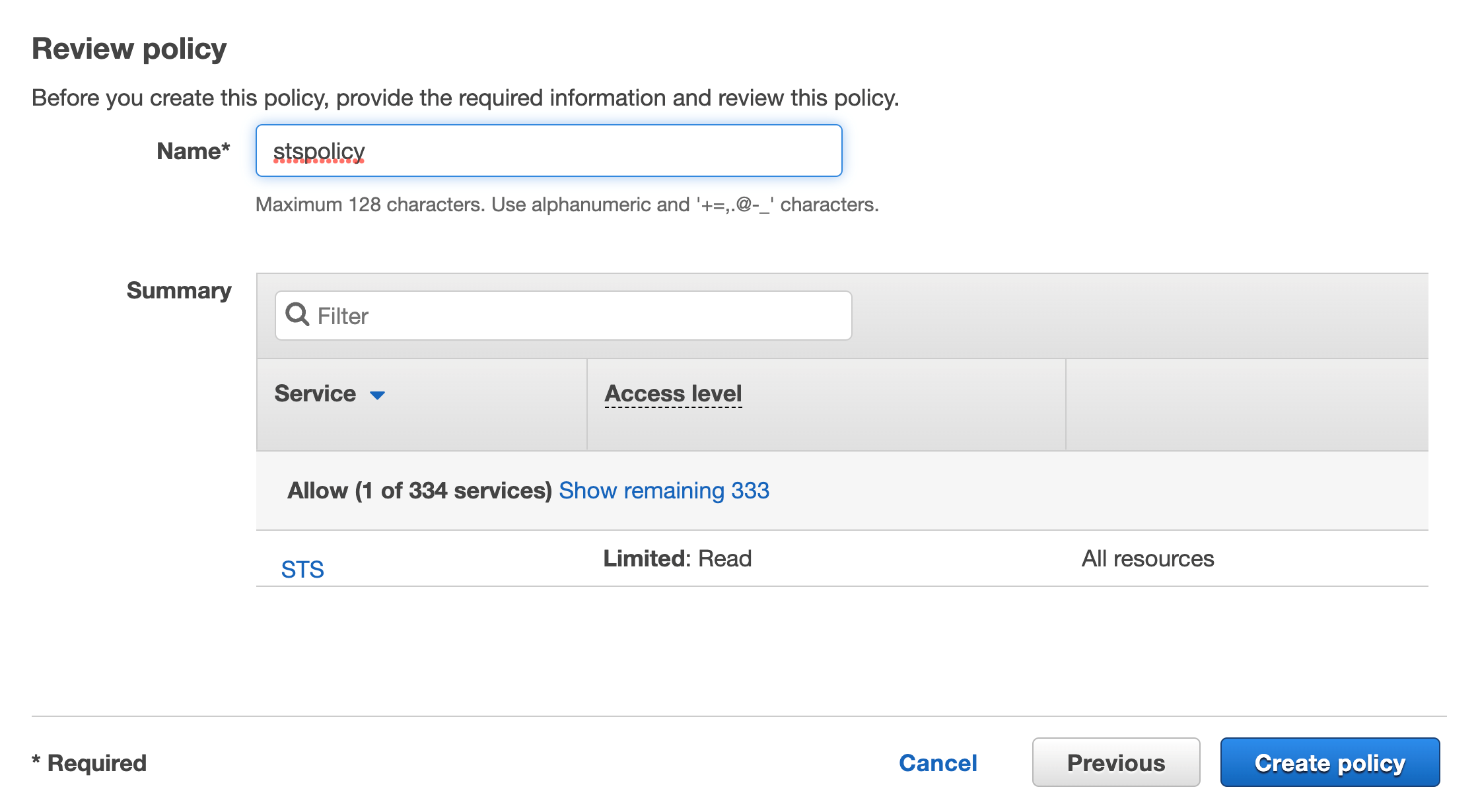
Click Browse, add a name and then click Create Policy
You should see a new internal rule added to the list
For the CodeArtifact action, you will do the same with this role, click Create built-in rules
Search for CodeArtifact in services, then select CodeArtifact
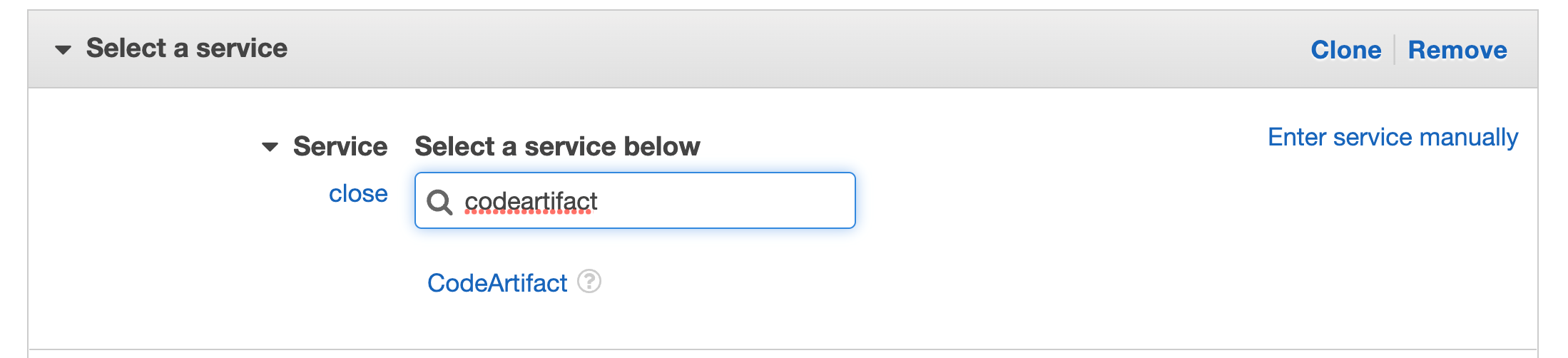
Search for "GetAuthorisationToken" in the actions and choose this action in the checkbox
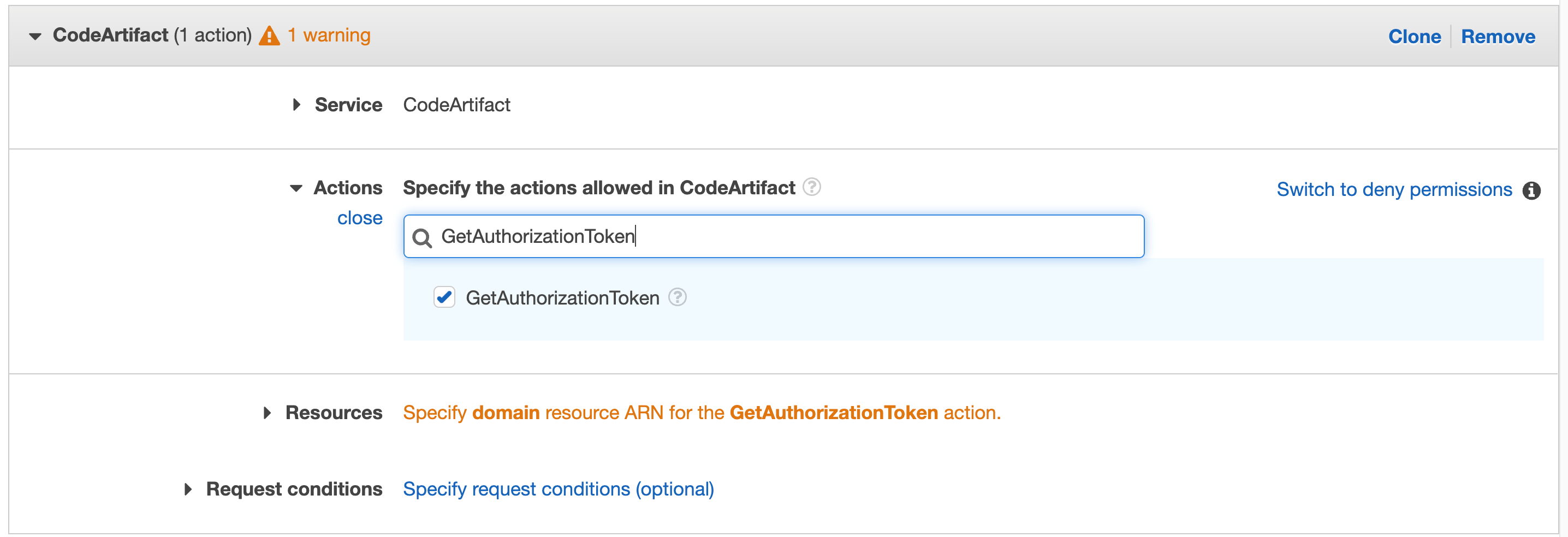
Repeat for "GetRepositoryEndpoint" and "ReadFromRepository"
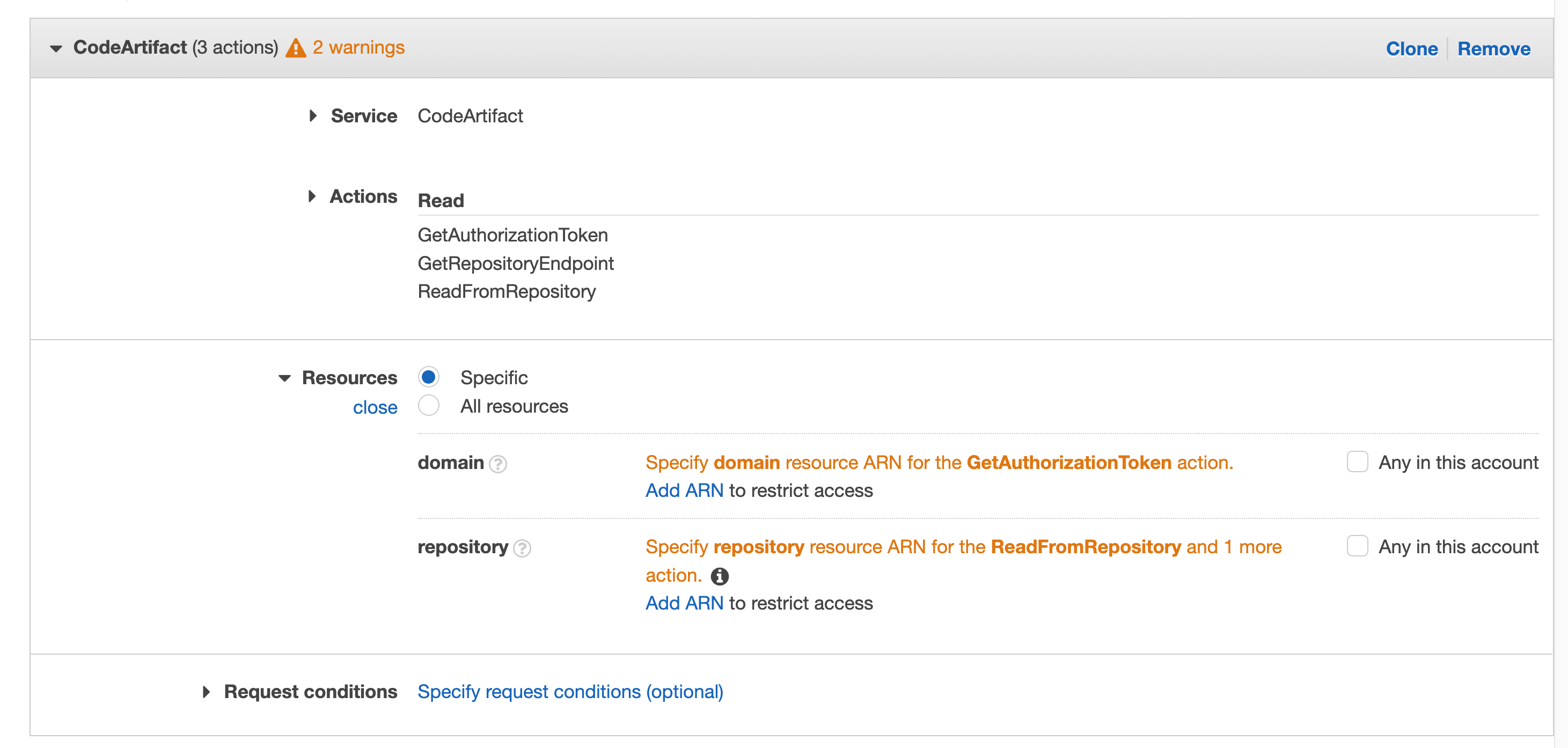
Click Resources to fix the 2 warnings and then click Add ARN on the first "Specify the ARN of the domain resource for the GetAuthorizationToken action".
You will get a pop-up window with fields for region, account, and domain name. Enter your region, account number, and the domain name you used as "private" when you created your domain earlier.
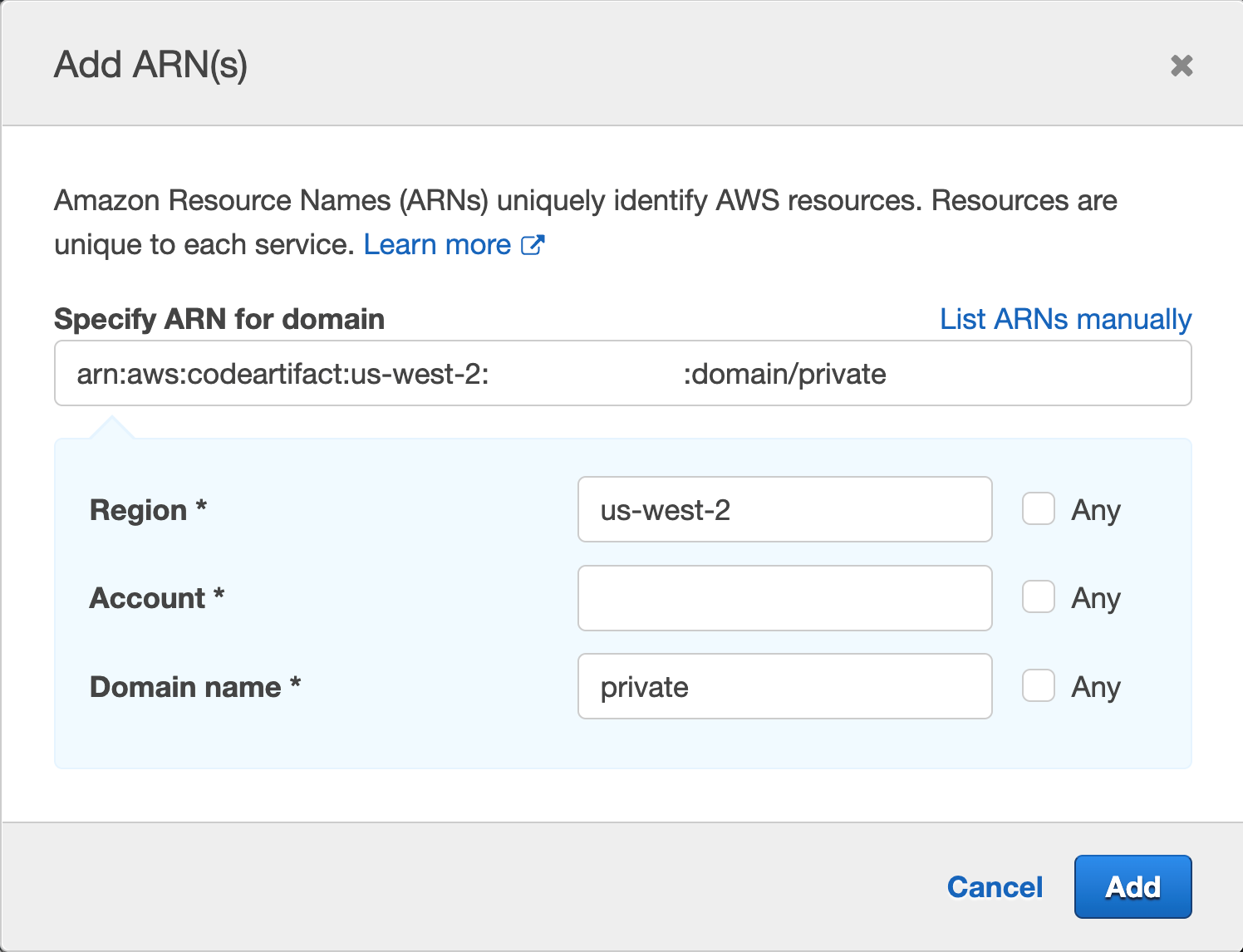
Then click Add
Repeat the same process for "Specify the ARN of the repository resource for ReadFromRepository and one more." This time, the authors will enter Region, Account ID, Domain Name, and Repository Name; we used "Private" for the repository they created earlier and "private" for the domain.
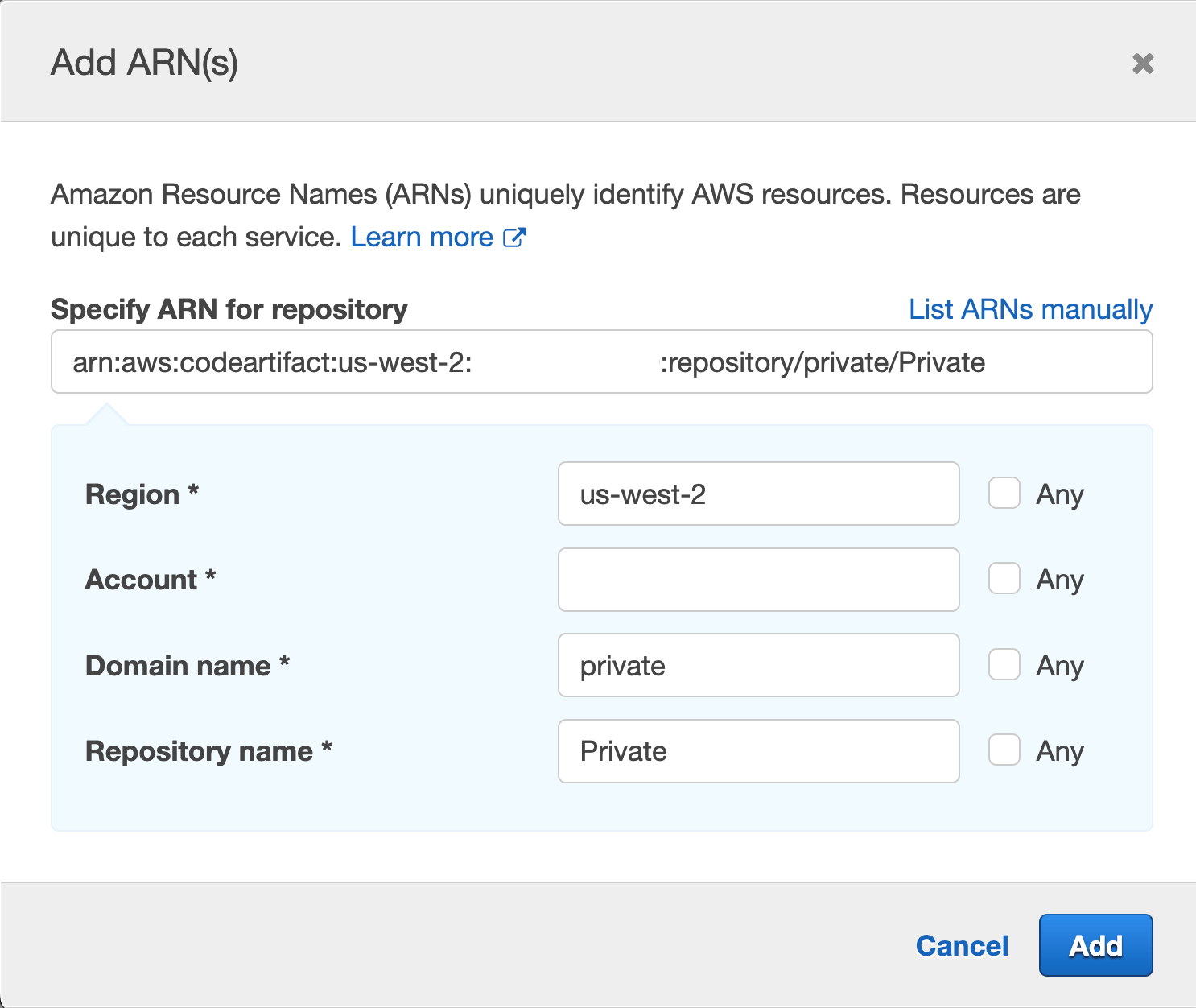
Remember that it is best practice to specify the resource you are targeting. You can tick the 'Any' box, but you aim to narrow the scope of the IAM role as best you can.
9. Go to CodeCommit, then click on the repository you created earlier in step 1
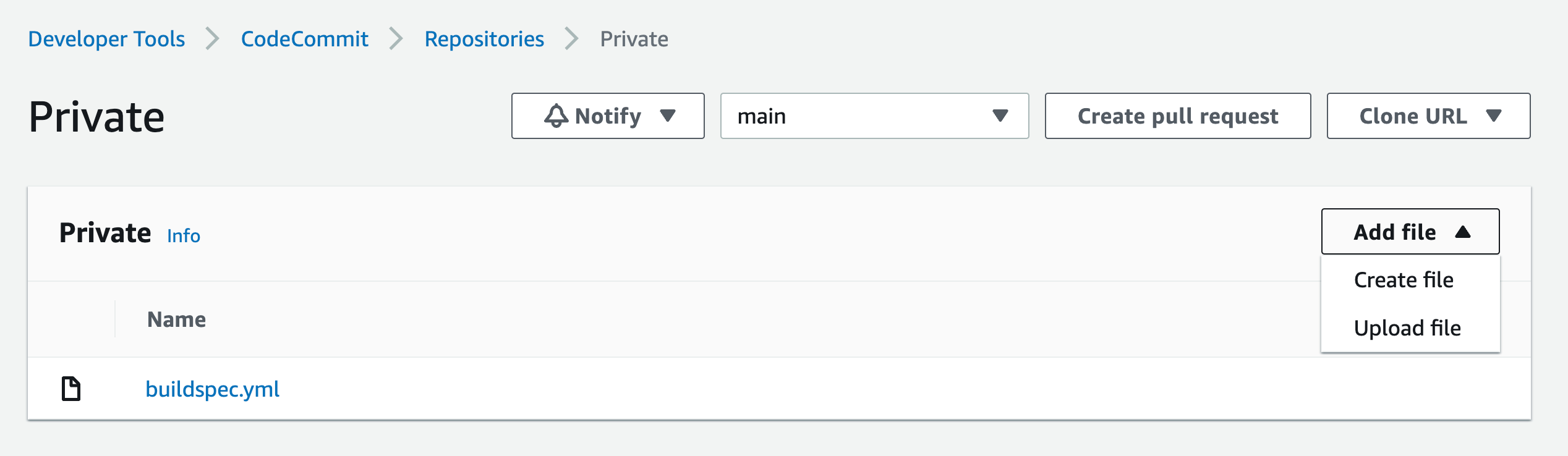
Click on the Add File drop-down list, then click on the Create File button
Paste the following in the editor area:
{
"dependencies": {
"mathjs": "^11.2.0"
}
}
Name the file "package.json"
Add your name, email address and an optional approval message
Repeat this process for "index.js" and paste the following in the editor area:
const { sqrt } = require('mathjs')
console.log(sqrt(49).toString())
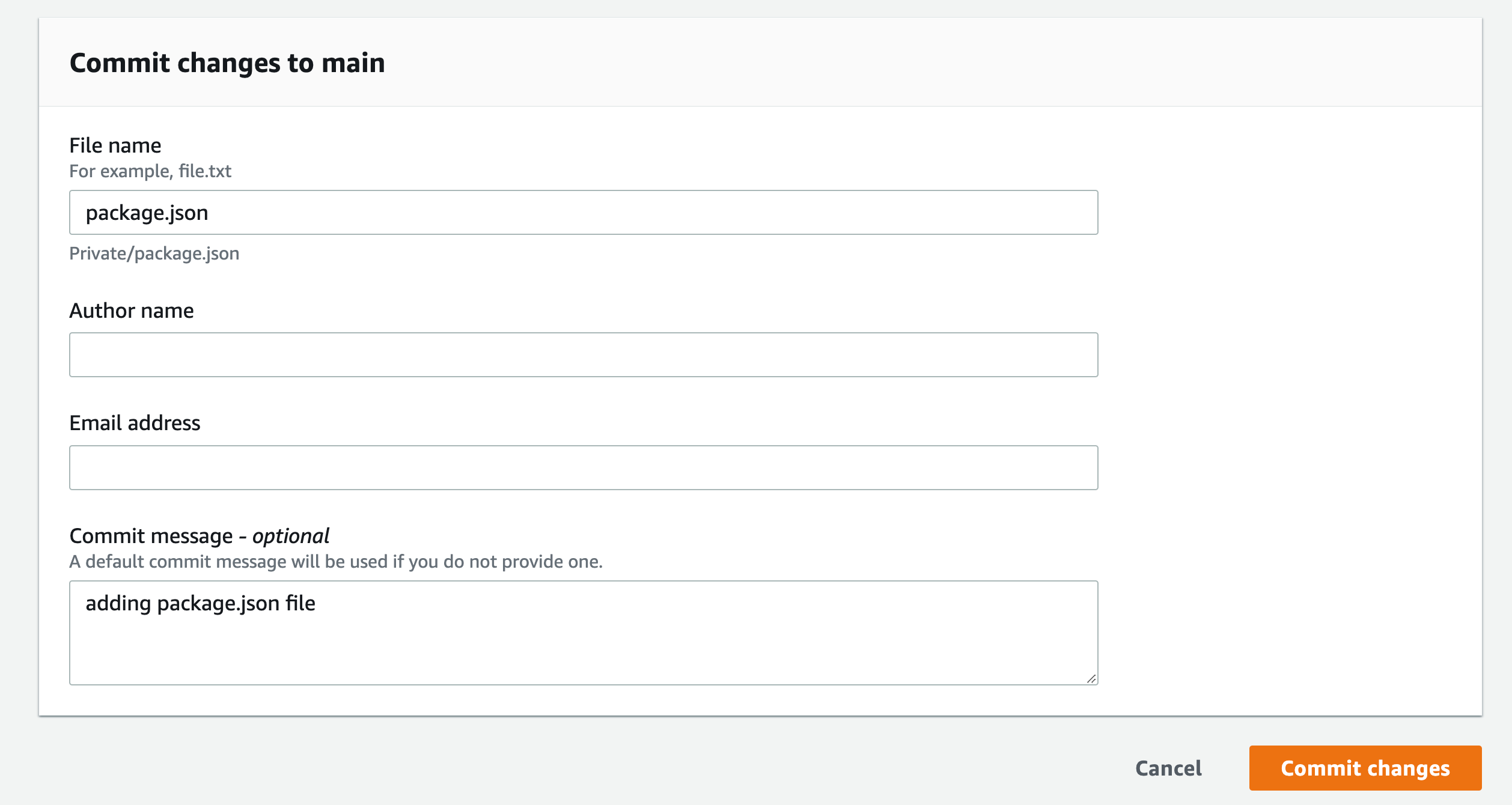
This will launch the pipeline and start building the application.
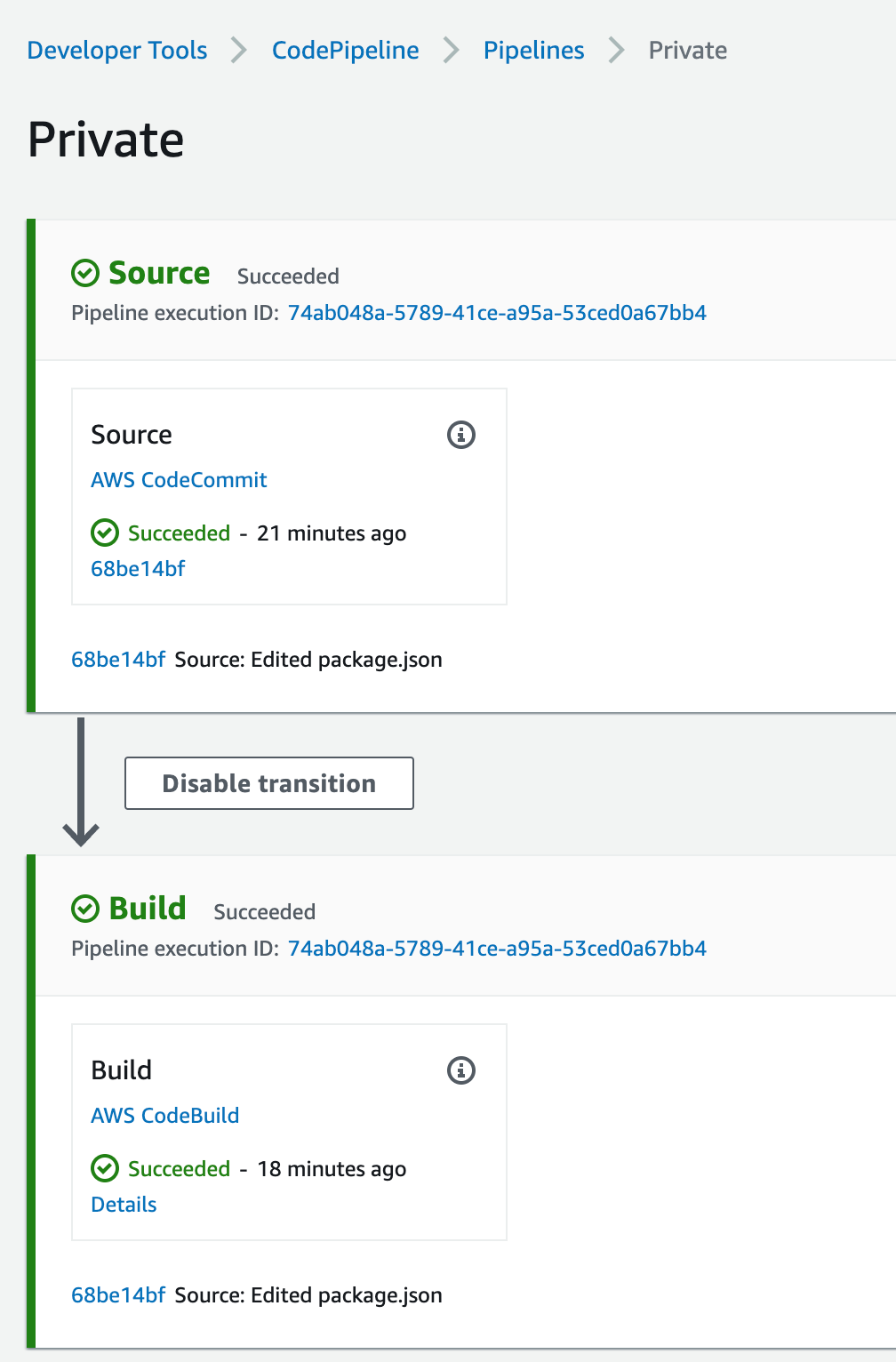
This straightforward application gets the square root of 49 and logs it on the screen. If you click on the Details link from the pipeline build stage, you will see the result of the NodeJS application. The logs are stored in CloudWatch, and you can navigate there by clicking the View entire log link: "Showing the last xx lines of the build log. View the entire log."
We used the npm example in buildspec.yml above; a similar configuration will be used for pip and twine.
You must set the environment variables, change the settings.xml, and build for Maven, Gradle, and NuGet.gradle files, and install the plugin for your IDE environment. For more information, click here.
Arranging
Navigate to the VPC endpoint from the AWS console and delete the endpoints you have created.
Go to CodePipeline and delete the pipeline created.
Go to CodeBuild and delete the compile project created.
Go to CodeCommit and delete the created repository.
Go to CodeArtifact and delete the repository and the created domain.
Go to IAM and delete the roles created:
For CodeBuild: codebuild--service-role
For CodePipeline: AWSCodePipelineServiceRole--.
Summary
In this article, we implemented a complete CI/CD pipeline with CodePipeline coordinating CodeBuild to build and test a small NodeJS application using CodeArtifact to download the application code dependencies. This was all done without going on the public internet and maintaining logs in CloudWatch.



